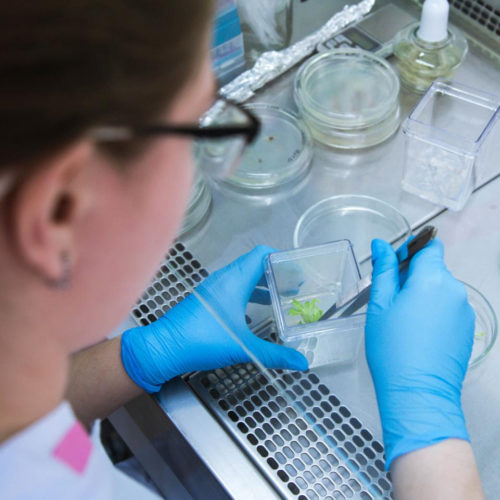
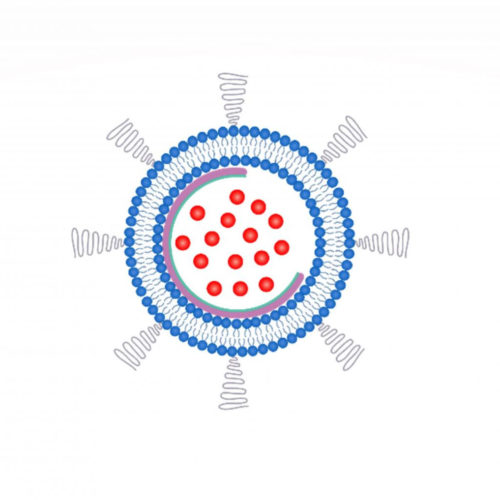
For decades, scientists have explored the use of liposomes — hollow spheres made of lipid bilayers — to deliver chemotherapy drugs to tumor cells. But drugs can sometimes leak out of liposomes before they reach their destination, reducing the dose received by the tumor and causing side effects in healthy tissues. Now, researchers report in...
Tag: <span>scientific</span>
Russian scientists improved the way of treatment of phenylketonuria
The inherited disease of phenylketonuria is expressed in the inability of the body to absorb certain amino acids, mainly phenylalanine The inherited disease of phenylketonuria is expressed in the inability of the body to absorb certain amino acids, mainly phenylalanine. A person affected by this disease has to follow a low-protein diet all his life....
Adult skates can spontaneously repair cartilage injuries
Researchers have found that adult skates have the ability to spontaneously repair injured cartilage, using a type of cartilage stem cell. Human cartilage has very limited capacity for repair, and the finding may lead to new stem cell treatments for human cartilage injuries. Published in the journal eLife, the study identified a new type of...
What is the Secretome?
By Reginald Davey Reviewed by Dr. Mary Cooke, Ph.D. Biological organisms are incredibly complex machines made up of innumerable parts working in complementary ways. Understanding the complex, intricate interactions between tissues and cells is, therefore, key to a holistic understanding of the organism as a whole, and over the centuries that have encompassed the science...
Trial questions benefits of organic nitrates for bone health
Several clinical trials have reported beneficial effects of organic nitrates on bone health, which could lead to a reduced risk of fractures. Some of these trials have been retracted because of scientific misconduct; however. A new study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research found that organic nitrates do not have clinically relevant...
Unexpectedly potent protein droplets help explain hereditary diseases
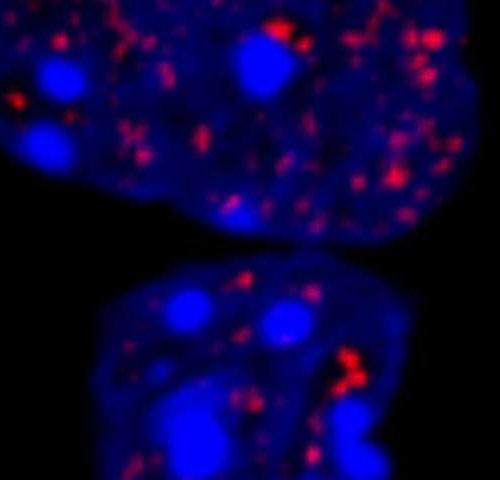
by Max Planck Society Microscopic image of cell nuclei of cultured cells. HOXD13 condensates are labelled in red. The DNA is stained in blue. Credit: MPI f. Molecular Genetics/ Shaon Basu Repeats of individual building blocks within proteins are the cause of many hereditary diseases, but how such repeats actually cause disease is still largely...
Researchers unravel protein mystery of three brain diseases
by KU Leuven Microscopic image of mouse neurons to which the patient-derived α-synuclein protein was administered. The protein deposits (green) form after seven days. Credit: Microscopy by Anke Van der Perren The accumulation of one particular protein in the brain is the basis of three very different age-related conditions. Until recently, nobody understood how this...
Drug reduces the risk of child sexual abuse
Technology Org Science and technology news Drug reduces the risk of child sexual abuse Posted Today A drug that lowers levels of the male hormone testosterone in the body reduces the risk of men with pedophilic disorder sexually abusing children, a study from Karolinska Institutet published in the journal JAMA Psychiatry shows. About one in...
Sensor detects biomarker of early-stage multiple sclerosis
Diagnostic strategy developed by Brazilian researchers can also be used to distinguish MS from neuromyelitis optica, another demyelinating disorder. The two diseases have similar symptoms but must be treated differently. FUNDAÇÃO DE AMPARO À PESQUISA DO ESTADO DE SÃO PAULO Researchers at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar) in Sorocaba (state of São Paulo,...
Study finds evidence for existence of elusive ‘metabolon’
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — For more than 40 years, scientists have hypothesized the existence of enzyme clusters, or “metabolons,” in facilitating various processes within cells. Using a novel imaging technology combined with mass spectrometry, researchers at Penn State, for the first time, have directly observed functional metabolons involved in generating purines, the most abundant cellular...