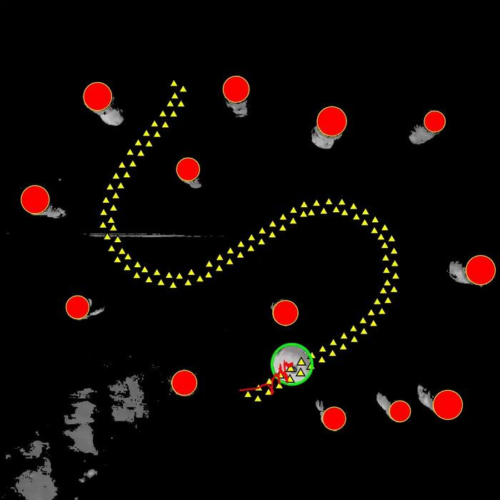
NEWS RELEASE 25-JUN-2024 EPFL researchers have succeeded in directing floating objects around an aquatic obstacle course using only soundwaves. Their novel, optics-inspired method holds great promise for biomedical applications such as noninvasive targeted drug delivery. Peer-Reviewed PublicationECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FÉDÉRALE DE LAUSANNE VIDEO: MOVING AN OBJECT WITH SOUNDWAVES DESPITE DISORDER © LWE EPFL view moreCREDIT: ©...
Tag: <span>Sound</span>
Researchers discover how sound reduces pain in mice
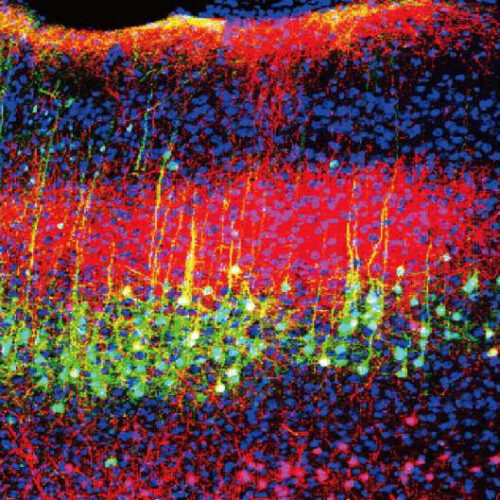
by National Institutes of Health Sound reduces pain in mice by lowering the activity of neurons in the brain’s auditory cortex (green and magenta) that project to the thalamus. Credit: Wenjie Zhou An international team of scientists has identified the neural mechanisms through which sound blunts pain in mice. The findings, which could inform development...
Sound can directly affect balance and lead to risk of falling
What people hear and do not hear can have a direct effect on their balance, according to new research from the New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mount Sinai (NYEE). The research, published in the March 12 issue of JAMA Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, provides a better understanding of the relationship between hearing loss...
Researchers find the brain processes sight and sound in same manner
Although sight is a much different sense than sound, Georgetown University Medical Center neuroscientists have found that the human brain learns to make sense of these stimuli in the same way. The researchers say in a two-step process, neurons in one area of the brain learn the representation of the stimuli, and another area categorizes...