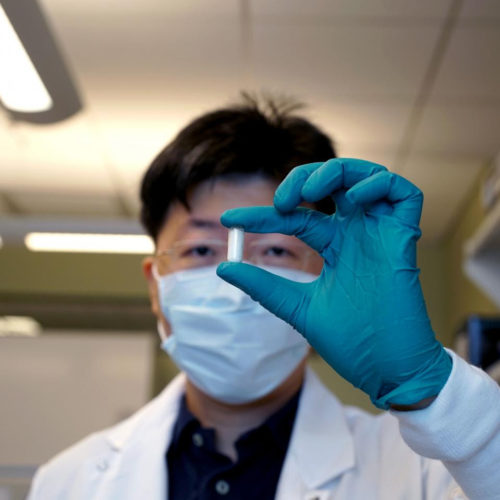
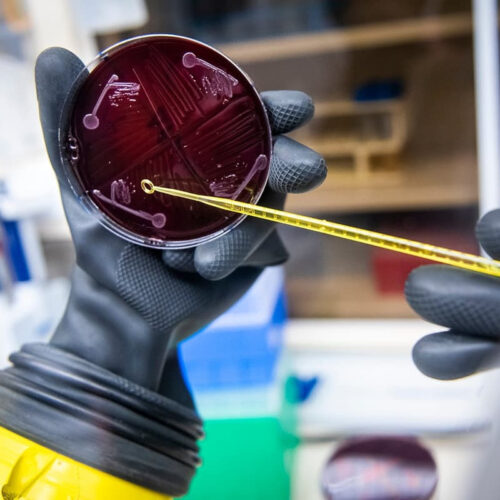
A team of researchers in the UK have injected lab-grown blood into humans for the first time, the BBC reports, in a demonstration of potentially game-changing medical tech that could end scarcity of rare blood types. The rarest blood types go far beyond the more conventional blood type groups, such as A, B, AB, and O. Some,...
Tag: <span>Synthetic</span>
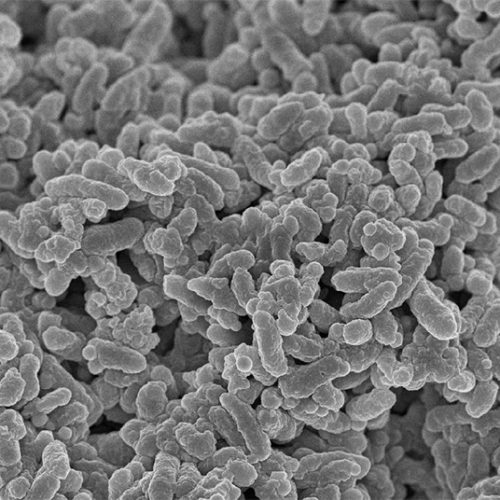
Stanford scientists build first synthetic human microbiome from scratch
By Rich Haridy September 11, 2022 Researchers combined around 100 of the most prevalent bacterial species into a model of the human microbiome that can successfully colonize mouse models for future studies L.A. Cicero A team of researchers from Stanford University has constructed the first synthetic microbiome model, built entirely from scratch and encompassing more...
Synthetic coating for the GI tract could deliver drugs or aid in digestion
MIT engineers devise a temporary film that may help treat diabetes, infections, and other conditions MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY POSTDOCTORAL ASSOCIATE JUNWEI LI, LEAD AUTHOR OF THE STUDY, HOLDS AN EXAMPLE OF A CAPSULE CONTAINING THEIR ENZYME. CREDIT: IMAGE BY MELANIE GONICK/MIT By making use of enzymes found in the digestive tract, MIT engineers have...
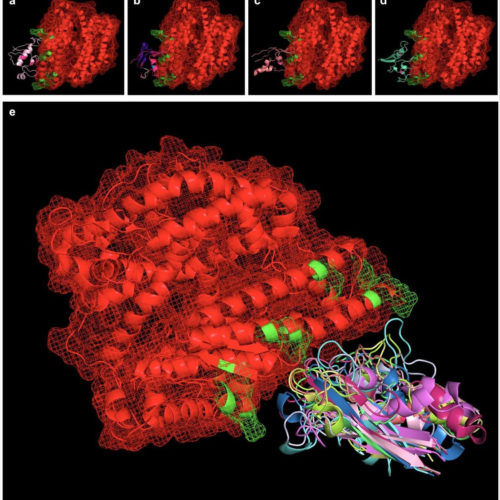
Synthetic drug ebselen could be repurposed to treat SARS-CoV-2 by targeting main protease at distant
Molecular characterization of ebselen binding activity to SARS-CoV-2 main protease AMERICAN ASSOCIATION FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF SCIENCE The synthetic drug ebselen can bind to both the catalytic region and a previously unknown distant site on the SARS-CoV-2 virus’ main protease, according to a molecular simulation analysis of the drug’s interactions with this enzyme. The results...
New ‘molecular computers’ find the right cells
by University of Washington An artist’s depiction of a Co-LOCKR nano-device coming together on the surface of a cell that has the right combination of cell surface markers. Credit: UW Medicine Institute for Protein Design Scientists have demonstrated a new way to precisely target cells by distinguishing them from neighboring cells that look quite similar....
Cutting edge synthetic peptides block SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
By Sally Robertson, B.Sc. Researchers at Ligandal Inc., the University of California San Francisco and Toyota Technological Institute at Chicago, have designed novel synthetic peptides that potently inhibit the ability of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) to infect host cells. The team’s SARS-BLOCK™ peptides competitively inhibit the receptor-binding domain (RBD) on the SARS-CoV-2...
Scientists develop synthetic blood-thinner that doesn’t cause bleeding side-effects
by Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne gulation factor XII (FXII), and the mice without the enzyme had a highly reduced risk of thrombosis without bleeding side-effects. The discovery triggered a race for FXII inhibitors. The Laboratory of Therapeutic Proteins and Peptides of Professor Christian Heinis at EPFL has now developed the first synthetic inhibitor of...
Scientists work to freeze-dry synthetic platelets
A Case Western Reserve University scientist, who has for more than a decade pioneered research into synthetic platelet substitutes, has been awarded a $3.8 million grant by the U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) to develop freeze-dried artificial platelets that can treat bleeding in wounded soldiers in the battlefield before they can be taken to a...
Exhaled biomarkers can reveal lung disease
Specialized nanoparticles create a ‘breath signal’ that could be used to diagnose pneumonia and other infectious or genetic diseases MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MA — Using specialized nanoparticles, MIT engineers have developed a way to monitor pneumonia or other lung diseases by analyzing the breath exhaled by the patient. In a study of mice,...
Synthetic Melanin Protects from Radiation Damage
JULY 14TH, 2020 SIAVASH PARKHIDEHCARDIAC SURGERY, DENTISTRY, DERMATOLOGY, MATERIALS, NUCLEAR MEDICINE, ONCOLOGY, ORTHOPEDIC SURGERY, PUBLIC HEALTH, RADIATION ONCOLOGY, RADIOLOGY, SPACE MEDICINE Researchers at Northwestern University have developed a new biomaterial, selenomelanin, that can help protect people from radiation. The new substance, chemically synthesized and produced by bacteria, helps protect cells from radiation more effectively than...
- 1
- 2