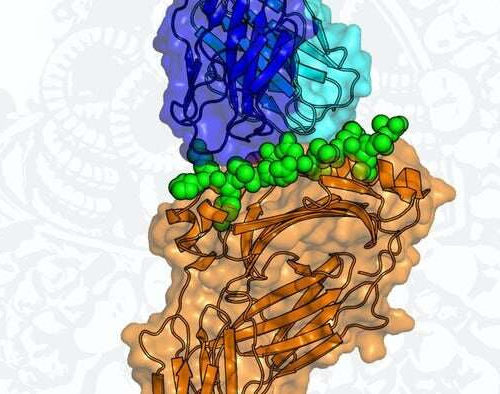
UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH FRANK DIXON CHAIR IN CANCER IMMUNOLOGY, UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH SCHOOL OF MEDICINE, AND CO-LEADER, CANCER IMMUNOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY PROGRAM, UPMC HILLMAN CANCER CENTER. view more CREDIT: UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH PITTSBURGH, July 15, 2020 – Blocking a newly identified “immune memory checkpoint” in immune cells could improve immunotherapy and help prevent cancers from...
Tag: <span>T-cells</span>
Discovery of new immune targets inside flu virus offers hope for universal vaccine
by Cardiff University New markers hidden inside the influenza virus have been discovered by scientists at Cardiff University. The researchers from the School of Medicine worked with an international team of experts—including collaborators in Moscow, Russia and Melbourne, Australia—to look at how people’s immune systems responded to the new proteinmarkers. They showed for the first...
Engineered killer immune cells target tumours and their immunosuppressive allies
Natural killer immune cells engineered to target the PD-L1 molecule can directly kill tumour cells in mice and reduce the numbers of immunosuppressive cells harbouring PD-L1 in mice and humans Scientists have engineered natural killer immune cells that not only kill head and neck tumour cells in mice but also reduce the immune-suppressing myeloid cells...
A key gene modifies regulatory T cells to fine-tune the immune response
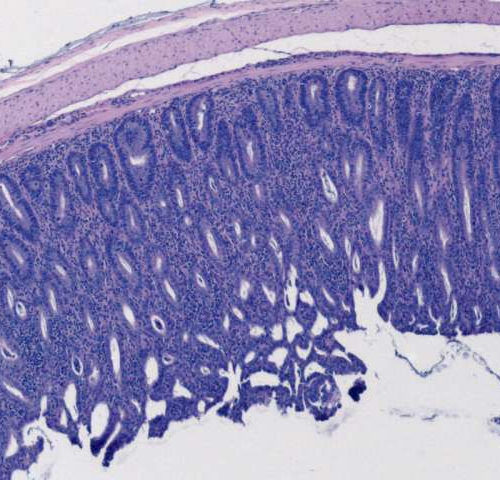
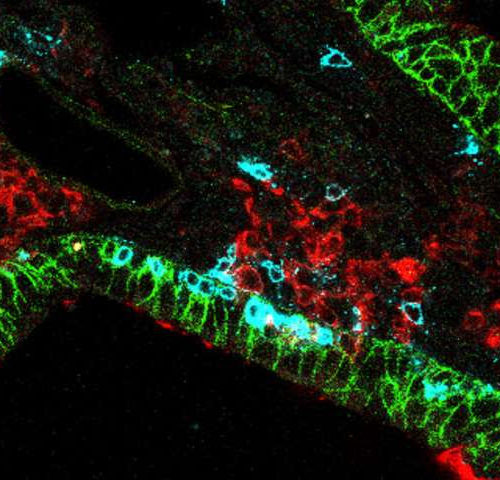
by Salk Institute A histology image showing inflammation in colon epithelium. Weakening of regulatory T cell function induces infiltration of immune cells (small blue dots) into colon epithelium (blue layer) and causes colitis. Credit: Salk Institute The human immune system is a finely-tuned machine, balancing when to release a cellular army to deal with pathogens,...
Blood cell mutations linked to leukemias are inevitable as we age
by RIKEN A new study by researchers at the RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Science in Japan reports differences in blood cell mutations between Japanese and European populations. The study found that these pre-clinical mutations were strongly associated with different types of cancers and can explain why Europeans have higher rates of chronic lymphocytic leukemia,...
Could the cure for IBD be inside your mouth?
by University of Michigan While many people put off their regular trips to the dentist, recent research has shown that the consequences of doing so may go beyond cavities and root canals. From heart disease to diabetes, poor oral health is often a reflection of a person’s overall health and may even be the cause...
How targeting killer T cells in the lungs could lead to immunity against respiratory viruses
by Salk Institute A significant site of damage during COVID-19 infection is the lungs. Understanding how the lungs’ immune cells are responding to viral infections could help scientists develop a vaccine. Now, a team of researchers led by Salk Professor Susan Kaech has discovered that the cellsresponsible for long-term immunity in the lungs can be...
How T cells make sure they have quiet time
All cells, like all people, need “quiet” time to function properly, and this is particularly true of T cells, one of the immune system’s main weapons. They must be ready for activation at all times, and primed to divide more rapidly than almost any cell in the body. When T cells are overworked, people can...
New Insights: Armies of strategically stationed T cells fight viral infections, cancer
by Delthia Ricks , Medical Xpress The immune system mounts robust responses to infections, vaccines and cancer, but only now have scientists fully begun to unravel how non-circulating populations of T cells that reside in the body’s “mucosal barrier tissues” keeps threats at bay. While an academic focus on non-circulating T cellsin mucosal tissues may...
Technique identifies T cells primed for certain allergies or infections
by Anne Trafton, Massachusetts Institute of Technology MIT researchers have developed a method to isolate T cells that bind to different targets and then sequence their RNA. Credit: SciStories LLC When your immune system is exposed to a vaccine, an allergen, or an infectious microbe, subsets of T cells that can recognize a foreign intruder leap into action....