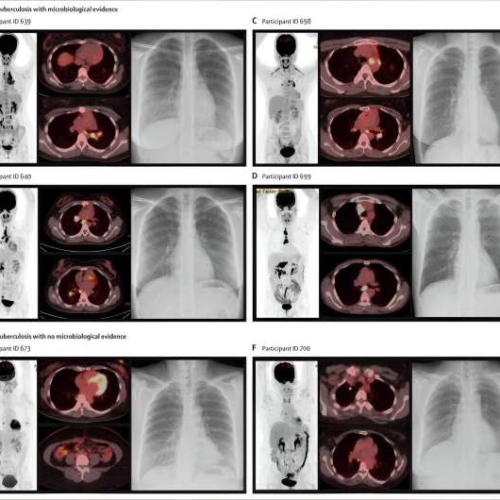
by University Hospitals of Leicester NHS Trust Baseline [18F]FDG-PET-CT and chest radiograph features of incipient tuberculosis. Credit: The Lancet Microbe (2024). DOI: 10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00289-6A novel approach to studying the progression of tuberculosis (TB) from infection to disease has identified and treated people at increased risk of developing the disease that current methods of testing would not.Researchers...
Tag: <span>TB</span>
Scientists invent single rapid test for both HIV and TB
by Tulane University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Researchers at Tulane have developed a new and rapid test that can detect both HIV and tuberculosis at the same time with just a small amount of blood. In a paper published in Clinical Chemistry, researchers led by Tony Hu, Weatherhead Presidential Chair in Biotechnology Innovation and director of...
Stanford-led study shows kids exposed to TB at higher risk of disease than thought
Young children exposed to tuberculosis are at a surprisingly high risk of developing the disease, according to research led by the School of Medicine. The findings, which were published online in The Lancet, come from the largest modern study to assess TB risk among children closely exposed to the disease. TB kills more people than...
TB could be conquered by common painkillers, research reveals
by Freshscience Credit: CC0 Public Domain Aspirin could be used to treat the world’s deadliest infectious disease, according to new research conducted by Dr. Elinor Hortle at the Centenary Institute in Sydney. Tuberculosis—which affects a third of the global population—currently kills two million people every year. The spread of multi-drug resistant strains mean antibiotics are becoming less...
Immune System Targets Vitamin B12 Pathway to Neutralize Tuberculosis Bacteria
Close to 1.8 billion people worldwide are infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), the common and occasionally deadly bacterium that causes millions of cases of tuberculosis each year. The bacteria, having coevolved with humans over millennia, have devised ways of hijacking nutrients from its human host for its own benefit. Humans have equally complex ways of...
Anti-arthritis drug also stops tuberculosis bacillus from multiplying in blood stem cells
KU LEUVEN Immunologist Johan Van Weyenbergh (KU Leuven) and his Belgian-Brazilian colleagues have shown that a drug used to fight arthritis also stops the process that allows the tuberculosis bacillus to infect and hijack blood stem cells. Tuberculosis (TB) may affect any part of the body, but the spread of the disease might start in the bone marrow. Immunologists from KU Leuven and Brazil have shown that the...
Tuberculous infection is not life-long in most people
Penn-led study suggested majority will not develop disease even if test shows positive results UNIVERSITY OF PENNSYLVANIA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE PHILADELPHIA – A new analysis challenges the longstanding notion that tuberculous infection is a life-long infection that could strike at any time and cause tuberculosis (TB). Based on a review of clinical studies, researchers from...
The 10-cent tuberculosis test that’s saving lives
by Layne Cameron, Evangelyn Alocilja, Michigan State University News of a cure for the deadliest strain of tuberculosis is making headlines around the world. However, before treatment can begin, TB must first be diagnosed. Early detection has been a serious challenge for those suffering at various stages of this epidemic. Until now. A colorimetric biosensing...
New blood test for human tuberculosis may also identify people at most risk
by National Institute for Health Research A new study conducted by researchers in Leicester and Nottingham has shown the potential for a new blood test to not only diagnose human tuberculosis (TB) but also identify those at most risk of developing the disease, according to findings published in medical journal Clinical Infectious Diseases. Despite recent reductions,...
Standard TB tests may not detect infection in certain exposed individuals
Study published in Nature Medicine UNIVERSITY HOSPITALS CLEVELAND MEDICAL CENTER CLEVELAND – An international collaboration of infectious disease experts has identified a large group of people who appear to have naturally mounted an immune response to TB, a bacterial infection that is the leading cause of infectious disease death worldwide. Nearly 200 people from 2500 households with active TB were...
- 1
- 2