October 1, 2024 by McMaster University In a study published in the journal Cell Reports Medicine, researchers Sheila Singh and Jakob Magolan discovered a critical vulnerability in metastatic brain cancer, which they say can be exploited with new drugs to prevent spread. Singh, a professor in McMaster’s Department of Surgery and director of the Center...
Tag: <span>therapeutic</span>
MAIT cells can be tuned to fight different pathogens via their metabolism, leading to new therapeutic strategies
by La Jolla Institute for Immunology Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain A population of unconventional white blood cells has recently captured the attention of immunologists and clinicians alike. Unlike conventional T cells, which circulate throughout the body in our blood, mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells are largely found in tissues where they provide immune protection against a...
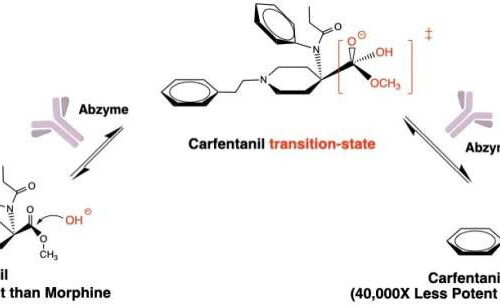
Therapeutic can seek and destroy potent opioid to treat overdoses
by The Scripps Research Institute A biologic (abzyme) developed by Scripps chemists converts the ultra-potent opioid carfentanil (left) to a weaker version (right) by stabilizing the reaction’s transition-state (center). Utilizing abzymes could lead to new ways for treating synthetic opioid overdose. Credit: Kim Janda, PhD, Scripps Research A new therapeutic designed by Scripps Research chemists can alter the molecular structure of...
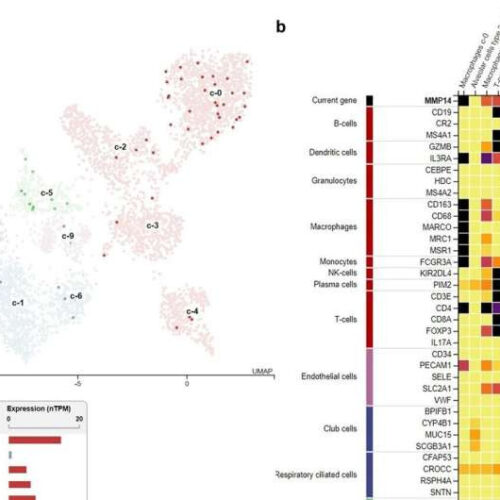
Teams identifies cell entry mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 and therapeutic target for COVID-19
by Hong Kong Baptist University MT1-MMP+ACE2+ lung epithelial cells are susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection. a MT1-MMP+ cells were distributed across the indicated cell types in the human lung within UMAP. b Heat map analysis of MMP14 gene expression in various lung and airway cells. c The distribution of ACE2+ and ACE2+ MT1-MMP+ cells in the lung was assessed using human...
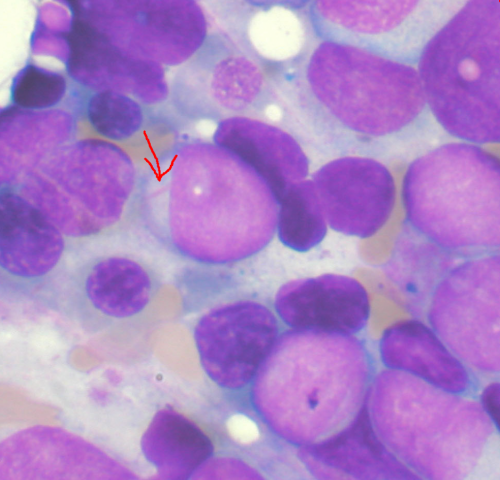
New therapeutic approach against leukemia
by Max Planck Society Bone marrow aspirate showing acute myeloid leukemia. Several blasts have Auer rods. Leukemia frequently originates from the so-called leukemic stem cell, which resides in a tumor promoting and protecting niche within the bone marrow. Scientists from the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry in Martinsried, Germany, have found a new way to make...
Predicting therapeutic response in depressed teen girls
by Elsevier The risk of developing major depressive disorder (MDD) surges during adolescence–particularly for girls. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can be an effective treatment, but only about half of girls diagnosed with depression show significant improvement. Researchers at Harvard Medical School and McLean Hospital have now identified a non-invasive test of brain function that could help...
Signalling research waves red flag for commercial drug target candidate
by Babraham Institute Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Researchers at the Babraham Institute have used their understanding of cellular signaling to highlight a pitfall in an emerging treatment for cancer and inflammation. A new review just published in Biochemical Society Transactions summarizes the researchers’ current knowledge, which includes details of their research published in Nature Communicationsearlier this year....
Study leads to potential for new treatment approach to Alzheimer’s
by University of Kentucky Research looking at a possible new therapeutic approach for Alzheimer’s disease was recently published in the Journal of Neuroinflammation. The paper out of the University of Kentucky’s Sanders-Brown Center on Aging (SBCoA) is titled “Therapeutic Trem2 activation ameliorates amyloid-beta deposition and improves cognition in the 5XFAD model of amyloid deposition”. The...
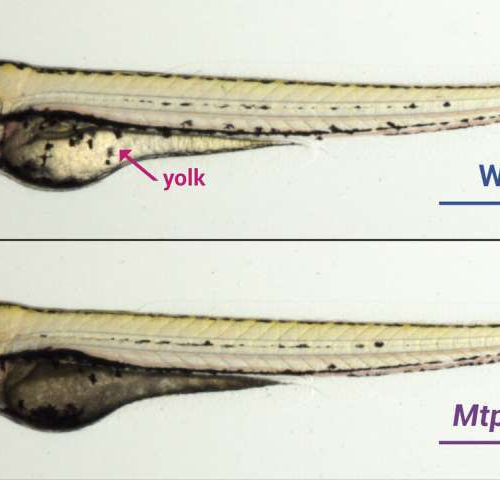
Newly discovered mutation could point to heart disease therapeutic target
by Carnegie Institution for Science lipid from the yolk of a zebrafish through the circulation to the growing tissues of the embryo. Later in development, they will also carry lipids from the intestine and liver. While normal, wild-type, zebrafish have clear yolks (top image), zebrafish with mutations in Mtp have abnormally opaque yolks because they...
Surrogate coronavirus may help researchers discover therapies and vaccines
by Albert Einstein College of Medicine To study the potentially lethal coronavirus, Albert Einstein College of Medicine scientists have turned a relatively harmless virus into a coronavirus “surrogate” that is much safer to work with. The research was described this month in Cell Host & Microbe. “Research on the ‘real’ coronavirus is limited by the...