Synthetic compound could serve as prototype for a novel class of drugs to treat neurological damage DZNE – GERMAN CENTER FOR NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASES Researchers from the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE), UK and Japan have developed a neurologically acting protein and tested it in laboratory studies. In mice, the experimental compound ameliorated symptoms of...
Tag: <span>Therapeutics</span>
Vaccine against grass pollen allergy as potential treatment for chronic hepatitis B
by Johannes Angerer, Medical University of Vienna Chronic hepatitis B infections represent a global health problem that could hitherto only be treated by chemotherapy. A team of researchers led by Rudolf Valenta from MedUni Vienna’s Center for Pathophysiology, Infectiology and Immunology has now demonstrated that a protein contained in the BM32 vaccine against grass pollen...
Reviewing Associations Between Physical Activity and Loss of Average Telomere Length with Age
This news or article is intended for readers with certain scientific or professional knowledge in the field. Telomeres are repeated DNA sequences at the ends of chromosomes. With each cell division a little telomere length is lost, and this is an important part of the countdown mechanism that limits replication of somatic cells. Somatic cells...
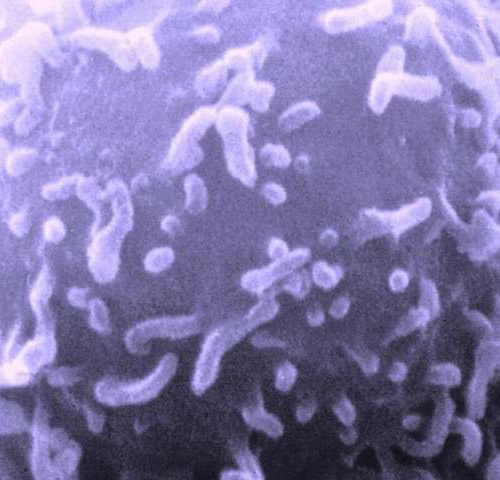
Designed bacteria produce coral-antibiotic
Sustainable biotechnological production of a natural substance against tuberculosis TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF MUNICH (TUM) HORN CORALS OF THE SPECIES ANTILLOGORGIA ELISABETHAE PRODUCE ANTIBIOTIC NATURAL SUBSTANCES. A RESEARCH TEAM AT TUM HAS SUCCESSFULLY PRODUCED ONE OF THESE SUBSTANCES IN THE LABORATORY. view more CREDIT: (IMAGE: THOMAS BRÜCK / TUM) Thomas Brück saw the sea whip Antillogorgia...
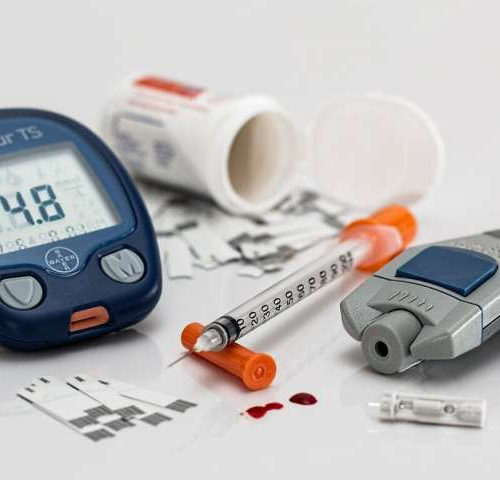
Smartphones may help detect diabetes
by University of California, San Francisco Researchers at UC San Francisco have developed a ‘digital biomarker’ that would use a smartphone’s built-in camera to detect Type 2 diabetes—one of the world’s top causes of disease and death—potentially providing a low-cost, in-home alternative to blood draws and clinic-based screening tools. Type 2 diabetes affects more than...
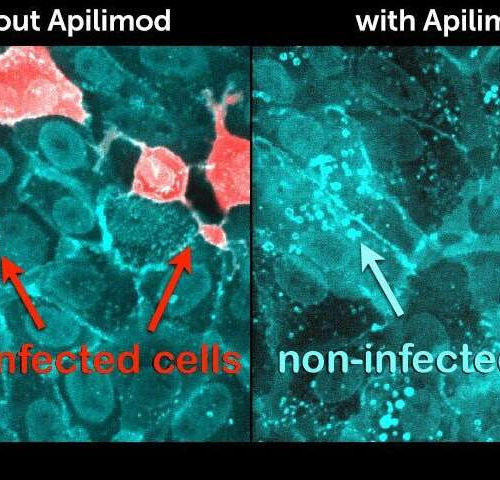
Two existing drugs point to a potential new target against COVID-19
by Alice McCarthy, Harvard Medical School Researchers have found that an existing drug, apilimod, prevented infection of human cells with the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Credit: Tomas Kirchhausen New lab-based studies show that two existing drugs, including one developed by a researcher at Harvard Medical School and Boston Children’s Hospital, inhibit SARS-CoV-2—the virus that causes COVID-19—from infecting...
Fighting cancer with rejection-resistant, ‘off-the-shelf’ therapeutic T cells
by Ana María Rodríguez, Ph.D., Baylor College of Medicine Scanning electron microscopy image of a human lymphocyte. Credit: National Cancer Institute Personalized cancer treatments are no longer just options of the future. In the past few years, researchers have made significant progress in ‘teaching’ the body’s immune T cells to recognize and kill specific cancer...
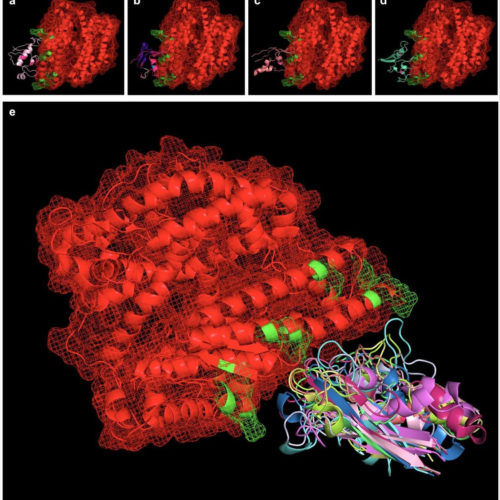
The behaviour of therapeutic antibodies in immunotherapy
Since the late 1990s, immunotherapy has been the frontline treatment against lymphomas where synthetic antibodies are used to stop the proliferation of cancerous white blood cells. However, in the more than 20 years since their use began, the molecular mechanisms that underlie this therapy are still little understood. For the first time, scientists from the...
Identifying Alzheimer’s risk factors in young people
Interview conducted by Emily Henderson, B.Sc. News-Medical speaks to Dr. Keith Fargo from the Alzheimer’s association about their latest research which looked at risk factors that could aid in the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. Why is it important to research Alzheimer’s and its risk factors? Alzheimer’s is a huge problem. It is a fatal...
Cutting edge synthetic peptides block SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
By Sally Robertson, B.Sc. Researchers at Ligandal Inc., the University of California San Francisco and Toyota Technological Institute at Chicago, have designed novel synthetic peptides that potently inhibit the ability of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) to infect host cells. The team’s SARS-BLOCK™ peptides competitively inhibit the receptor-binding domain (RBD) on the SARS-CoV-2...