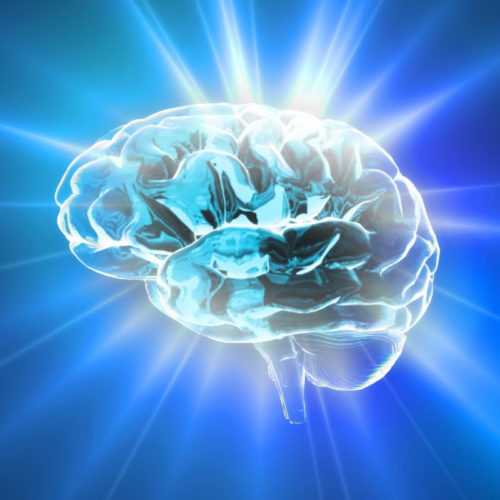
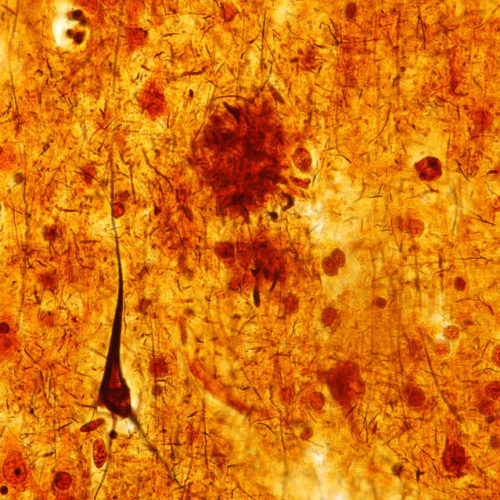
JON HAMILTON This light micrograph from the brain of someone who died with Alzheimer’s disease shows the plaques and neurofibrillary tangles that are typical of the disease. A glitch that prevents healthy cell structures from transitioning from one phase to the next might contribute to the tangles, researchers say. Jose Luis Calvo/ Science Source The...
Tag: <span>Therapeutics</span>
Researchers develop peptides for treating gastrointestinal disorders
Reviewed by James Ives, M.Psych. (Editor) Milestone for therapeutic development of peptides against gastrointestinal disorders The fascinating family of trefoil factor peptides brings hope to both research and industry to improve the treatment of chronic disorders such as Crohn’s disease. For the first time, a team led by ERC awardee Markus Muttenthaler from the Faculty...
New light shed on link between Alzheimer’s and liver disease
By Rich Haridy July 06, 2020 New research from the University of South Carolina is uncovering exactly how non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) influences the neurological conditions associated with Alzheimer’s disease. The study describes how a certain protein produced in the liver can travel to the brain and trigger neuroinflammation. Several recent studies have drawn...
Blocking cholesterol storage could stop growth of pancreatic tumors
by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Organoids of mouse pancreatic tumor cells grown “ex vivo,” outside the body. Organoids are used as a model system to study tumor biology and treatments. Credit: Tobiloba Oni, Tuveson lab/CSHL Scientists at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) have found that they can stop the growth of pancreatic cancer cells by...
Nuclear Softening Allows Cells to Move Into Dense Tissue, Encouraging Injury Repair
Using an enzyme inhibitor in meniscus cells, a Penn team was able to soften their nucleus and promote access to previously impassible areas. By softening a cell’s nucleus so that it can squeeze its way through dense connective tissues, a group of researchers believes they’ve demonstrated a new way to help the body efficiently repair...
Discovery of new step in how brain cells work could lead to new therapies for epilepsy
by RCSI University of Medicine Researchers have identified a critical new step in how brain cells function in people with one of the most common forms of epilepsy. This could lead to new treatment approaches for people with drug-resistant epilepsy. The study was led by researchers at FutureNeuro, the SFI Research Centre for Chronic and...
Existing drugs can prevent SARS-CoV-2 from hijacking cells
by European Molecular Biology Laboratory An international team of researchers has analyzed how SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, hijacks the proteins in its target cells. The research, published in the journal Cell, shows how the virus shifts the cell’s activity to promote its own replication and to infect nearby cells. The scientists also identified...
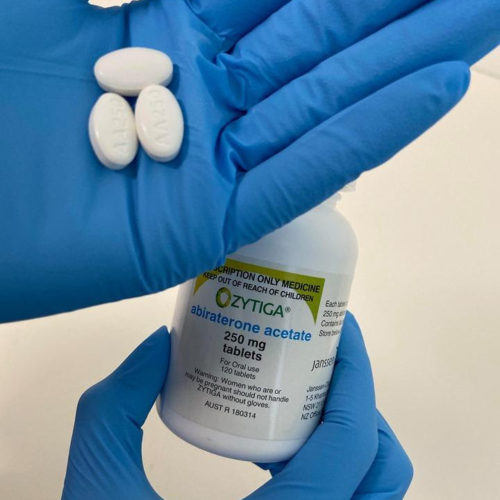
Breakthrough discovery to transform prostate cancer treatment
A NOVEL FORMULATION OF THE PROSTATE CANCER DRUG ABIRATERONE ACETATE – CURRENTLY MARKETED AS ZYTIGA – WILL DRAMATICALLY IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF LIFE FOR PEOPLE SUFFERING FROM PROSTATE CANCER.view more CREDIT: HAYLEY SCHULTZ/UNISA A novel formulation of the prostate cancer drug abiraterone acetate – currently marketed as Zytiga – will dramatically improve the quality of...
Nuclear softening allows cells to move into dense tissue, encouraging injury repair
by Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania By softening a cell’s nucleus so that it can squeeze its way through dense connective tissues, a group of researchers believe they’ve demonstrated a new way to help the body efficiently repair injuries. The team of researchers from the University of Pennsylvania tested this theory...
Virginia Tech scientists confirm usually harmless virus attacks the heart’s electrical system
Fralin Biomedical Research Institute scientists show adenovirus disrupts electrical signaling, impedes new communication channels. Credit: Fralin Biomedical Research Institute Adenovirus, which typically can cause a common cold, has a far more dangerous impact if it reaches the heart. When the virus commandeers gap junctions, it can slow production of connexin43, disturbing the electrical system that...