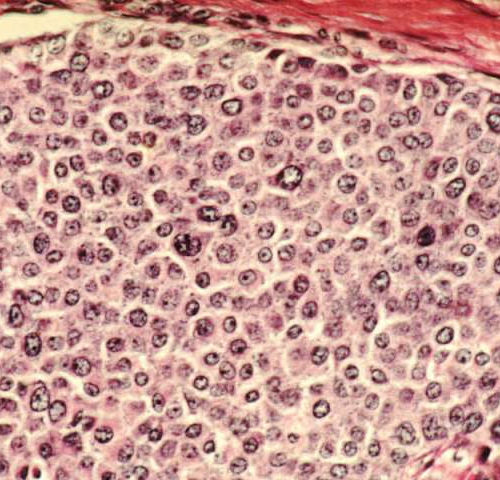
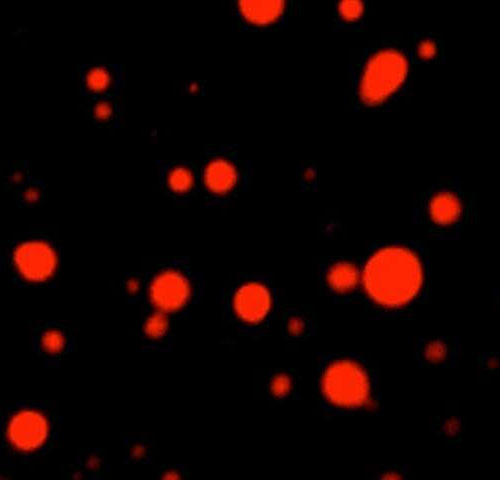
by University of Southern California The research team has discovered that akt-type cancer cells, which are common in breast cancer, above, can be killed by a common milk sugar, galactose. Credit: Wikimedia Commons Like any cells in the body, cancer cells need sugar—namely glucose—to fuel cell proliferation and growth. Cancer cells in particular metabolize glucose...
Tag: <span>Therapeutics</span>
How cells’ ‘lava lamp’ effect could make cancer drugs more powerful
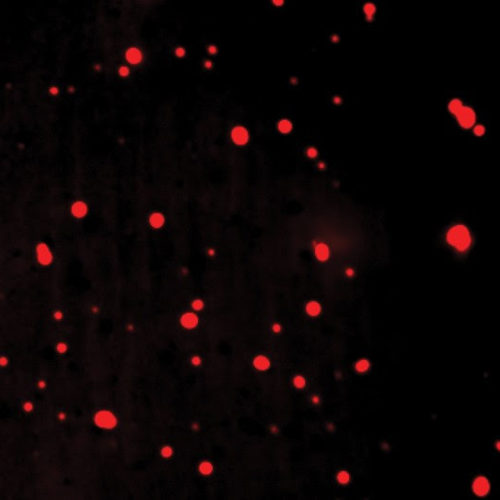
Discovery that synthetic compounds form concentrated droplets inside cells could shake up drug development — including the hunt for coronavirus treatments. Fluorescently tagged molecules of the cancer drug cisplatin clump up inside droplets in cells.Credit: Isaac Klein/Whitehead Institute There’s a long-standing assumption in the pharmaceutical industry that when drug molecules enter a cell, they spread...
COVID-19 immunology study reveals universally effective antibodies
A study of 149 people who have recovered from COVID-19 show that although the amount of antibodies they generated varies widely, most individuals had generated at least some that were intrinsically capable of neutralizing the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The findings are published in the journal Nature. Antibodies vary widely in their efficacy. While many may latch...
Early clinical trial supports tumor cell-based vaccine for mantle cell lymphoma
by Rockefeller University Press A phase I/II clinical trial by researchers at Stanford University suggests that vaccines prepared from a patient’s own tumor cells may prevent the incurable blood cancer mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) from returning after treatment. The study, which will be published June 19 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), reveals that...
How cancer drugs find their targets could lead to a new toolset for drug development
by Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research The molecular structure of the cancer drug cisplatin causes it to concentrate in tiny non-membrane bound organelles called condensates held together by the protein MED1. By altering other drugs to concentrate in specific condensates, drug developers may be able to improve targeting efficacy in future. Credit: Isaac Klein, Whitehead...
Cancer cells adapt to lack of key nutrient, posing potential problems for drugmakers
Cancer can adapt its metabolism in a way that could overcome lipid-focused therapies being developed by drug companies, a University of Toronto study has found. “Several clinical trials have failed because metabolism is such an adaptive process by which cancer cells gain drug resistance,” says Michael Aregger, a co-lead author and research associate who is...
Overactive enzyme causes hereditary hypertension
by Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine A Turkish family from a village near the Black Sea caught the attention of medical researchers in the early 1970s, when a physician discovered that many members of this large family had both unusually short fingers and astronomically high blood pressure, sometimes twice as high as that of...
Antihistamines and similar drugs could slow down Huntington’s disease
Controlling dopamine signalling by targeting the histamine receptor has been shown to be a promising strategy for preventing the progression of Huntington’s disease in mice Scientists have described a potential new therapeutic strategy for slowing down early-stage Huntington’s disease in a new study published today in eLife. The research in mice indicates that targeting the...
Missing sodium-channel component may protect against diet-induced artery stiffening
by American Physiological Society New research in mice finds that deficiency in one small component of a signaling pathway may protect against artery stiffening and subsequent kidney disease associated with a high-fat, high-sugar diet. The study is published in the American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology. Consuming a western diet—typically high in fat and refined carbohydrates,...
Microneedling therapeutic stem cells into damaged tissues
Small and minimally invasive ‘Detachable Microneedle Depots’ effectively deliver stem cells for localized MSC therapy of skin disorders Credit: Khademhosseini Lab (LOS ANGELES) — Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are multipotent in that they naturally replenish the cell types that build our bone, cartilage and adipose tissues. However, their much broader regenerative potential, based on their...