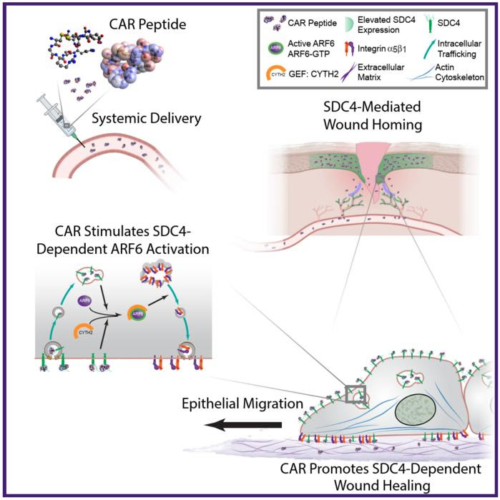
Peer-Reviewed Publication TAMPERE UNIVERSITY SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM HIGHLIGHTING PROPOSED MECHANISM OF ACTION OF CAR PEPTIDE. SYSTEMICALLY ADMINISTERED CAR PEPTIDE ASSOCIATES WITH THE HSPG SDC4, WHICH IS RESTRICTED TO EPIDERMIS AND BLOOD VESSELS IN MOUSE SKIN WOUNDS. CAR INDUCES SDC4-DEPENDENT ACTIVATION OF THE SMALL GTPASE ARF6, VIA THE GUANINE NUCLEOTIDE EXCHANGE FACTOR CYTH2, TO PROMOTE SDC4-, ARF6-...
Tag: <span>tissue repair</span>
Novel research demonstrates new method of spinal cord tissue repair
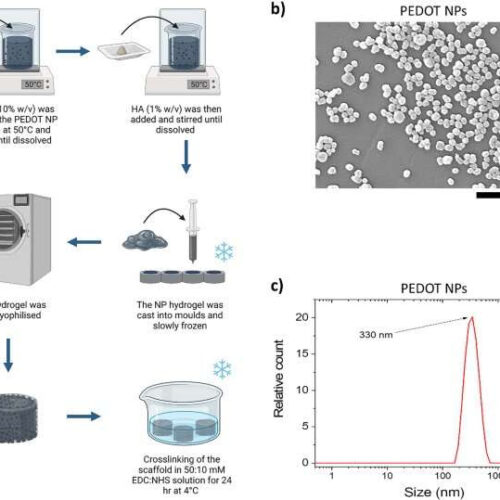
by University of Limerick a Synthesis schematic of gel:HA:PEDOT-NPs scaffolds. Incorporation of PEDOT NPs into Gel:HA hydrogel and processing by means of lyophilisation develops porous scaffolds, (image created with BioRender.com). b SEM images of synthesized PEDOT NPs. c DLS measurement of PEDOT NPs in the hydrodynamic state. Credit: Biomaterials Research (2022). DOI: 10.1186/s40824-022-00310-5 Unique new material developed...
P53 protein plays a key role in tissue repair, study finds
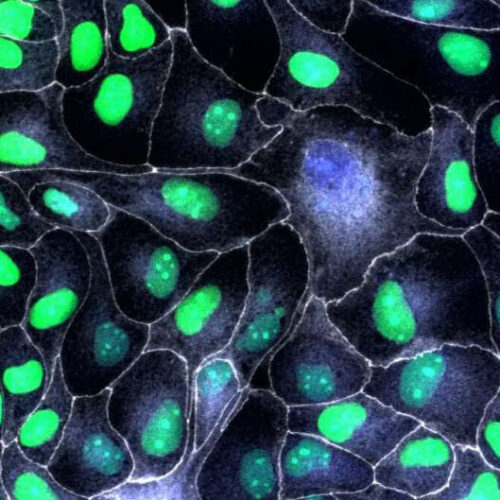
New research led by the University of Bristol has found the protein p53 plays a key role in epithelial migration and tissue repair. The findings could improve our understanding of the processes used by cells to repair tissues, and be used to identify interventions that could accelerate and improve wound repair. Epithelial tissues are the...
P53 protein plays a key role in tissue repair, study finds
by University of Bristol Once the collective migration of cells has closed the breach, the damaged leader cells need to be cleared from the tissue. When the leaders (blue nuclei) cannot be eliminated by their neighbours (green nuclei) their permanence in the epithelium compromises its regular architecture. Credit: University of Bristol New research led by...
Switching on tissue repair in IBD
Share on Pinterest Hinterhaus Productions/Getty Images In inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), the immune system attacks the cells that form the lining of the gut. This causes pain and discomfort. In a new study, scientists have identified a type of immune cell that can initiate repair of the gut lining following inflammation. Importantly, they have discovered...
Scientists switch on tissue repair in inflammatory bowel disease
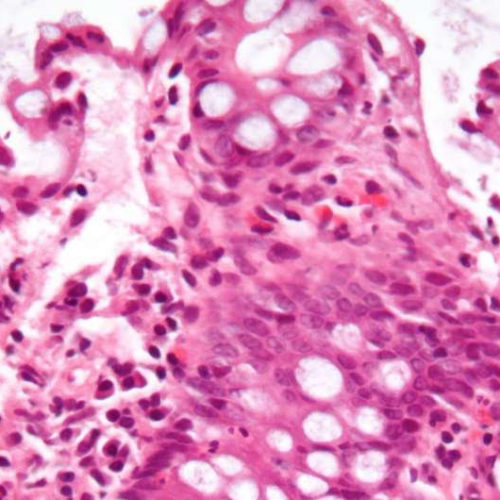
by KU Leuven Micrograph showing inflammation of the large bowel in a case of inflammatory bowel disease. Colonic biopsy. Credit: Wikipedia/CC BY-SA 3.0 A method that instructs immune system cells to help repair damaged tissues in the intestine has been developed by researchers at KU Leuven and Seoul National University. This opens the way for more effective treatment...
Study pinpoints target for managing inflammation, promoting tissue repair
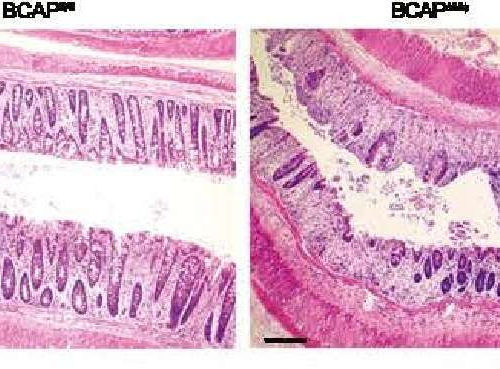
by Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center These histology images show that mice with dysfunctional BCAP protein were not able to repair their intestinal crypts during the recovery from infection. Managing the activity of the BCAP protein could help the body repair intestinal tissue from damage caused by inflammation, according to a new study led by experts...