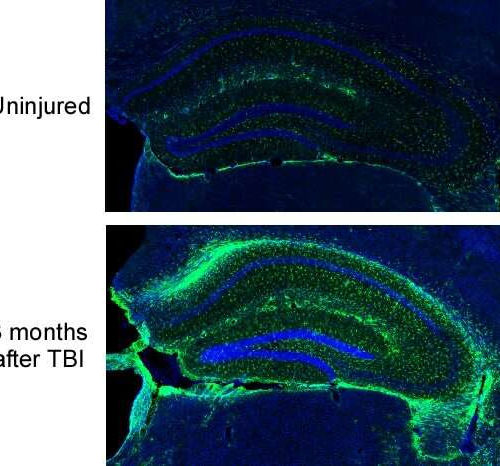
by Medical University of South Carolina Hippocampal slices of an uninjured brain (top) or a brain three months after TBI (bottom). There is an increase in astrocytes (green) following a brain injury. Credit: Dr. Stephen Tomlinson of the Medical College of Wisconsin. Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a major cause of disability and a risk factor...
Tag: <span>traumatic brain injury</span>
Researchers discover promising biomarkers to diagnose mild traumatic brain injury
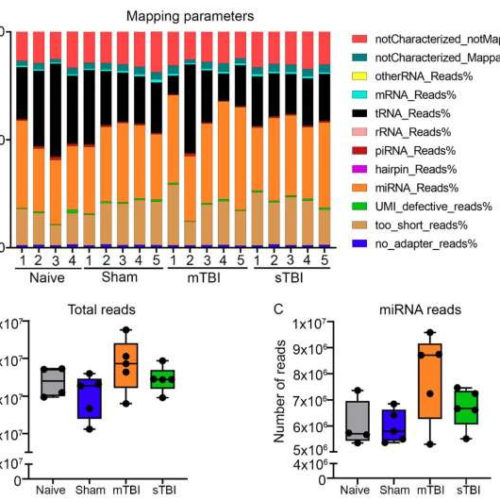
by University of Eastern Finland Figure 1: Primary quantification revealed no difference between the total sequenced reads and the sequenced reads mapping to miRNAs between experimental groups. (A) miRNA and transfer RNA reads comprised of 50–70% of the total sequenced reads (y-axis) across all samples in the experimental groups (x-axis; naïve n = 4, sham n...
Balance dysfunction after traumatic brain injury linked to diminished sensory acuity
KESSLER FOUNDATION IMAGE: DR. PILKAR IS A RESEARCH SCIENTIST IN THE CENTER FOR MOBILITY AND REHABILITATION ENGINEERING RESEARCH, AND DIRECTOR OF THE BALANCE AND ASSESSMENT LABORATORY AT KESSLER FOUNDATION. East Hanover, NJ. November 11, 2020. Kessler Foundation researchers have linked balance dysfunction in individuals with traumatic brain injury with diminished sensory acuity. This study used...
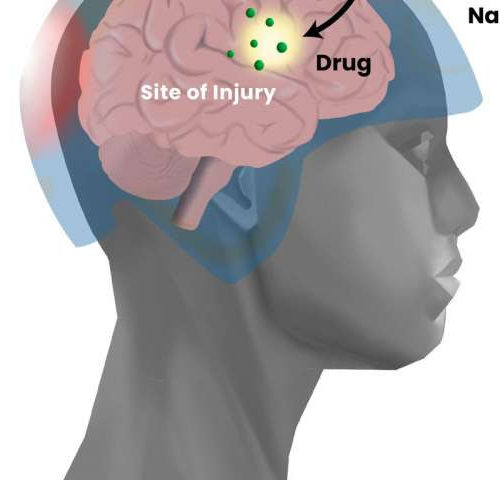
Development of precision drug delivery tool to treat traumatic brain injury
by Alexandra Demetriou, University of Southern California USC scientists have developed an experimental precision treatment for traumatic brain injury (TBI) that involves trapping therapeutic drugs in nanocage carriers before administering treatment. Near-infrared (NIR) light can safely penetrate the skull, and it can be used to “open” the nanocage to release drugs at the site of brain...
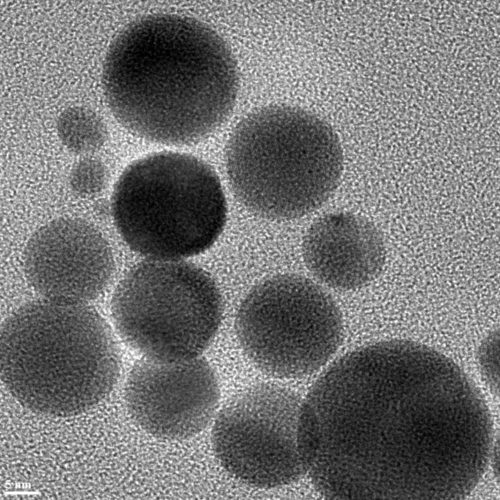
Charcoal a weapon to fight superoxide-induced disease, injury
Nanomaterials soak up radicals, could aid treatment of COVID-19 ARTIFICIAL ENZYMES MADE OF TREATED CHARCOAL, SEEN IN THIS ATOMIC FORCE MICROSCOPE IMAGE, COULD HAVE THE POWER TO CURTAIL DAMAGING LEVELS OF SUPEROXIDES. HOUSTON – (July 1, 2020) – Artificial enzymes made of treated charcoal could have the power to curtail damaging levels of superoxides, radical...
High doses of ketamine can temporarily switch off the brain, say researchers
by University of Cambridge Wikipedia Researchers have identified two brain phenomena that may explain some of the side-effects of ketamine. Their measurements of the brain waves of sheep sedated by the drug may explain the out-of-body experience and state of complete oblivion it can cause. In a study aimed at understanding the effect of therapeutic...
A new biomarker for the aging brain
by RIKEN Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics Research (BDR) in Japan have identified changes in the aging brain related to blood circulation. Published in the scientific journal Brain, the study found that natural age-related enlargement of the ventricles—a condition called ventriculomegaly—was associated with a lag in blood drainage from a specific deep...
Early intervention following traumatic brain injury reduces epilepsy risk
by Iqbal Pittalwala, University of California – Riverside A research team led by a scientist at the University of California, Riverside, has found that brains treated with certain drugs within a few days of an injury have a dramatically reduced risk of developing epilepsy later in life. The development of epilepsy is a major clinical...
Traumatic brain injury impairs hormone production, disrupting sleep, cognition, memory
by University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston More than 2.5 million people in the United States alone experience a traumatic brain injury, or TBI, each year. Some of these people are plagued by a seemingly unrelated cascade of health issues for years after their head injury, including fatigue, depression, anxiety, memory issues, and sleep...
Blue light can help heal mild traumatic brain injury
The Department of Defense has a vested interest in the new University of Arizona-led research, but the results have implications for civilians as well UNIVERSITY OF ARIZONA Early morning blue light exposure therapy can aid the healing process of people impact by mild traumatic brain injury, according to new research from the University of Arizona....