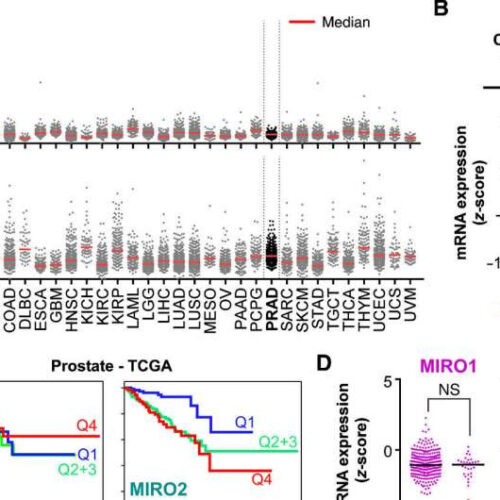
by Greg Glasgow, CU Anschutz Medical Campus MIRO1/2 alterations in cancer. A, The TCGA database was interrogated for MIRO1/2 mRNA expression across tumor types. PanCA, PanCancer. B, Relative expression of MIRO1/2 mRNA in cancer versus normal adjacent tissues on the prostate TCGA PanCancer study. C, Kaplan–Meier analyses based on MIRO1/2 mRNA expression in human primary...
Tag: <span>tumor cells</span>
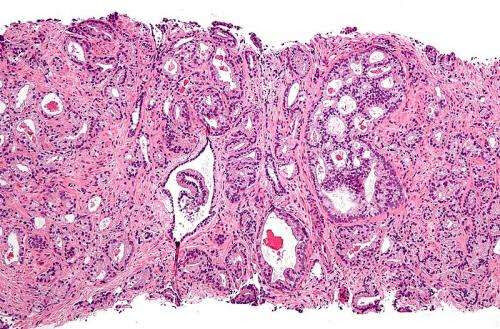
Early prostate cancers can harbor aggressive tumor cells
by Sarah Avery, Duke University Micrograph showing prostatic acinar adenocarcinoma (the most common form of prostate cancer) Credit: Wikipedia Many cases of early prostate cancer are dominated by cells that are slow-growing, often leading to a clinical decision to monitor for progression before initiating treatments that can have adverse side effects. But some of these...
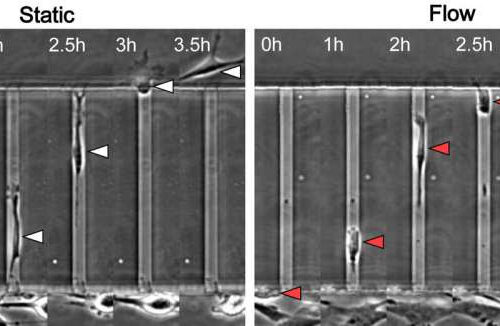
Protein appears to prevent tumor cells from spreading via blood vessels
by Johns Hopkins University In static conditions, cells enter microchannels, whereas 40-60% reverse direction when fluid is flowing. Courtesy of Johns Hopkins University. Credit: Johns Hopkins University Researchers have identified a specialized protein that appears to help prevent tumor cells from entering the bloodstream and spreading to other parts of the body. “We have discovered that this...
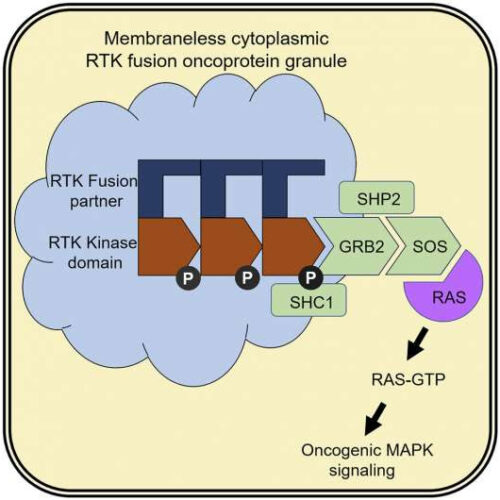
Novel structure found in tumor cells may open door to new kinds of cancer therapies
by Jason Alvarez, University of California, San Francisco Graphical abstract. Credit: Cell (2021). DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.031 In 2015, researchers at UC San Francisco found a structure inside of tumor cells that biologists had never seen before. Even more surprising, a closer examination of the structure revealed that it contained signaling proteins known as receptor tyrosine kinases, or RTKs, which were...
Tumor cells reveal a core syncytial drive to evade host defenses
by John Hewitt , Medical Xpress Credit: CC0 Public Domain Toxins, radiation, and normal metabolic processes together generate molecular lesions in every one of our cells to the tune of 10,000 to 1,000,000 hits per day. Fortunately, most of these code faults are immediately patched up by sophisticated DNA repair mechanisms. Any undetected damage to...
Alpha-ray missile therapy: Tumor cells attacked from intracellular region
by Osaka University Fig.1: The efficacy of 211At-AAMT using the PANC-1 xenograft model. Tumor growth inhibition by 211At-AAMT (left). Coronal images of 211At-AAMT in tumor-bearing model (right). Credit: Osaka University A cancer-specific L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1) is highly expressed in cancer tissues. Inhibiting the function of LAT1 has been known to have anti-tumor effects, but there has...
The bull’s eye: New modified stem cells can deliver drugs specifically to tumor cells
by Tokyo University of Science Credit: CC0 Public Domain As humans evolve, cancer also evolves in parallel, making the race for finding efficient treatment methods for cancer patients challenging and constant. In addition to designing drugs for treatment, the delivery of these drugs to targeted organs is also a major challenge faced by the cancer research...
Calcium bursts kill drug-resistant tumor cells
Multidrug resistance (MDR) – a process in which tumours become resistant to multiple medicines –– is the main cause of failure of cancer chemotherapy. Tumour cells often acquire MDR by boosting their production of proteins that pump drugs out of the cell, rendering the chemotherapies ineffective. Now, researchers reporting in ACS’ Nano Letters have developed nanoparticles that release bursts...
The combination of four drugs at low doses is more effective in the treatment of a lu
IDIBELL-BELLVITGE BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE BELLVITGE BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE (IDIBELL) view more CREDIT: BELLVITGE BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE (IDIBELL) Inhibit the specific activity of a protein affected by a mutation using high doses of a drug is the usual treatment for many cancers. Despite in the first instance this strategy is effective, leads to treatment resistance development...
Blocking sugar metabolism slows lung tumour growth
by Emily Packer, Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne Blocking a pair of sugar-transporting proteins may be a useful treatment approach for lung cancer, suggests a new study in mice and human cells published today in eLife. Cancer cells use a lot of sugar to fuel their rapid growth and spread. This has led scientists to...