ETH researchers have used computer simulations to show that tissue structure in different types of cancer is decisive in determining how a tumour develops. This information could make it possible to treat patients in a more targeted manner in future. The fact that every tumour is different makes cancer treatment one of the most complex...
Tag: <span>tumours</span>
Small particles in the blood can reveal early-stage cancer
Small particles released by cancer cells contain specific proteins that may be used in a blood test to detect cancer at an early stage, according to a study published in the scientific journal Cell by a group of investigators from US institutions, and including a principal author from LiU. Early detection of cancer increases the...
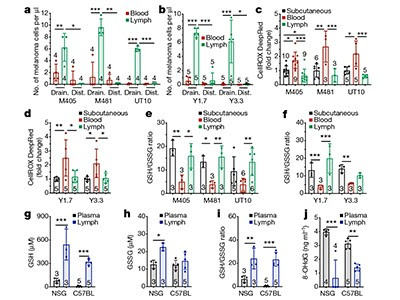
Cancer cells stock up in lymph vessels to survive
A cellular condition called oxidative stress can kill cancer cells. The finding that skin cancer cells evade such destruction using lipids acquired while passing through lymphatic vessels reveals a mechanism that boosts cancer spread. Barbara M. Grüner & Sarah-Maria Fendt PDF version The spread of cancer to distant parts of the body, such as to...
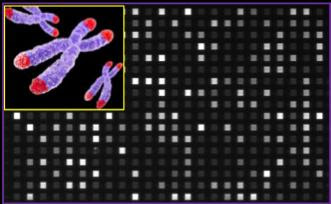
NUS researchers develop new system for accurate telomere profiling in less than 3 hours
The novel STAR assay can rapidly determine telomere dysregulation in cancers and age-related diseases in clinical settings A MAGNIFIED IMAGE CAPTURED BY THE DEVICE USED TO PERFORM STAR ASSAY. DIFFERENT FLUORESCENT INTENSITIES REFLECT THE LENGTH VARIATIONS IN INDIVIDUAL TELOMERE MOLECULES. view more CREDIT: NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE The plastic tips attached to the ends of...
New tool identifies which cancer patients are most likely to benefit from immunotherapy
A new prognostic tool developed by an international team led by CTI-Bath paves the way for personalised medicine for cancer patients. A new diagnostic tool that can predict whether a cancer patient would respond to immunotherapy treatment has been developed by scientists at the University of Bath. This advance in precision medicine will allow clinicians...
U of T researchers discover how to get more cancer-fighting nanoparticles to where they’re needed
Researchers in the University of Toronto’s Faculty of Applied Science & Engineering have discovered a dose threshold that greatly increases the delivery of cancer-fighting drugs into a tumour. The findings, published recently in the journal Nature Materials, provide a potentially universal method for gauging nanoparticle dosage and could help advance a new generation of cancer...
Immune cell steroids help tumours suppress the immune system, offering new immunotherapy targets
by Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute A study has revealed that tumors can evade the immune system by telling immune cells to produce immunosuppressive steroids. Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Department of Pathology, University of Cambridge, and MRC Cancer Unit, discovered that immune T cells from mouse skin and breast tumors secrete steroids, and that...
Patients who lived longer with cancer at greater risk of severe COVID-19 infection
KING’S COLLEGE LONDON Cancer patients diagnosed more than 24 months ago are more likely to have a severe COVID-19 infection, research has found. Cancer patients of Asian ethnicity or who were receiving palliative treatment for cancer were also at a higher risk of death from COVID-19. The research published today in Frontiers in Oncology by...
Five things you need to know about: mRNA vaccines
The race for a vaccine against the novel coronavirus, or SARS-CoV-2, is on, with 54 different vaccines under development, two of which are already being tested in humans, according to the World Health Organization. And among the different candidates is a new player on the scene – mRNA vaccines. According to Prof. Bekeredjian-Ding, an approved...
Five things you need to know about: mRNA vaccines
The race for a vaccine against the novel coronavirus, or SARS-CoV-2, is on, with 54 different vaccines under development, two of which are already being tested in humans, according to the World Health Organization. And among the different candidates is a new player on the scene – mRNA vaccines. One mRNA vaccine developed by US...