by Weill Cornell Medical College A stained graft which was retrieved six weeks after islet and reprogrammed vascular endothelial cell (R-VEC) co-transplantation. The white islet, revealed by insulin staining, is vascularized by green blood vessels derived from co-transplanted R-VECs, which are connected to host blood vessels (red). Credit: Dr. Ge Li Adding engineered human blood vessel-forming...
Tag: <span>type 1 diabetes</span>
Guidelines call for widespread Type 1 diabetes screening in children
by Bill Levesque, University of Florida Stages of type 1 diabetes. Credit: Hormone Research in Paediatrics (2024). DOI: 10.1159/000543035 A University of Florida Health physician-scientist led an international team of Type 1 diabetes experts who recently developed new treatment guidelines emphasizing wider screening for the disease among children and adolescents in the general population before symptoms arise. That...
Semaglutide can also be beneficial to people with type 1 diabetes, clinical trial finds
by McGill University Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Semaglutide (known by its brand name Ozempic) has gained widespread attention for its weight-loss benefits, but is officially approved for managing type 2 diabetes. While there is currently limited data on its risks and benefits for those with type 1 diabetes, new research offers promising insights. A new study...
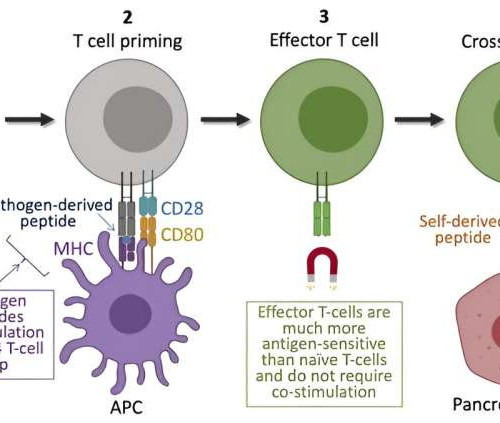
Bioengineering strategy uses immune-protected beta cell transplant to advance type 1 diabetes care
by Shawn Oberrath, Medical University of South Carolina Credit: Cell Reports (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114994 Regenerative medicine holds the extraordinary promise that future patients in need of new cells, tissues or organs will no longer have to rely on donors. Organ shortages and cell type mismatches will become past problems, replaced by safe, on-demand options for anyone who needs...
Transplanting insulin-making cells to treat Type 1 diabetes is challenging. Stem cells offer a potential improvement
by Vinny Negi, The Conversation Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Diabetes develops when the body fails to manage its blood glucose levels. One form of diabetes causes the body to not respond to insulin at all. Called Type 1 diabetes, or T1D, this autoimmune disease happens when the body’s defense system mistakes its own insulin-producing cells as foreign...
Off-label glucose-lowering drugs may put type 1 diabetes patients at risk
by Justin Jackson , Medical Xpress Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain A collaboration of researchers led by Emory University Rollins School of Public Health, Atlanta, is urging caution when prescribing off-label glucose-lowering drugs to individuals with type 1 diabetes (T1D). Both glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA) and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors have shown significant benefits...
Stem cell therapy reverses type 1 diabetes in world first
Credit: Cell (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.09.004 A groundbreaking discovery has recently brought hope to millions of people living with type 1 diabetes around the world. In a world first, scientists have successfully used stem cell therapy to reverse type 1 diabetes in a woman. This achievement is being hailed as a major medical breakthrough, as it offers a potential cure...
Research suggests a new strategy for people with type 1 diabetes to lower blood sugar after exercise
(A) Twenty-four-hour post-exercise continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). Each grey line represents 1 participant’s CGM trace for the 24-hour post-exercise period. (B) Comparison of 24-hour post-exercise median sensor glucose. Credit: Canadian Journal of Diabetes (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.jcjd.2024.05.001 Adults with type 1 diabetes should perform aerobic cooldowns to manage high blood sugar after intense exercise where glucose levels might rise,...
Bacterial infections could be trigger for type 1 diabetes, new research suggests
September 18, 2024 by Cardiff University Graphical abstract. Credit: Journal of Clinical Investigation (2024). DOI: 10.1172/JCI164535For the first time, scientists have found that proteins from bacteria can trigger the immune system to attack insulin-producing cells, leading to the development of type 1 diabetes. The new research showed that killer T-cells—a type of white blood cell...
Children less likely to have type 1 diabetes if mother has condition than if father is affected, study finds
July 26, 2024 by Diabetologia Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public DomainNew research to be presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD; Madrid, 9–13 September) shows that a child is almost twice as likely to develop type 1 diabetes (T1D) if their father has the condition, than if their...