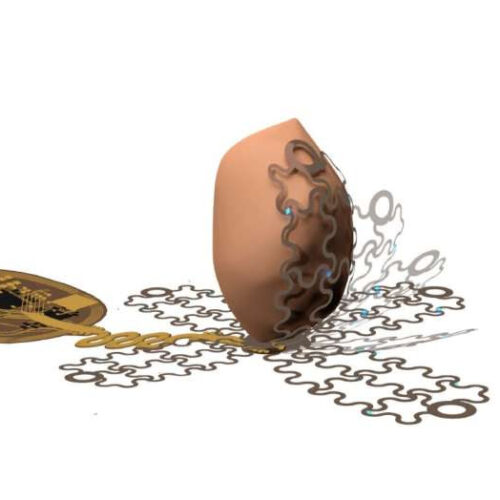
by Emily Dieckman, University of Arizona An artist’s rendering shows how a new pacemaker, designed by a UArizona-led team of researchers, is able to envelop the heart. The wireless, battery-free pacemaker could be implanted with a less invasive procedure than currently possible and would cause patients less pain. Credit: Philipp Gutruff Atrial fibrillation—a form of...
Preliminary data suggest that ROS1 inhibitor, NVL-520, is well-tolerated and active in non-small cell lung cancer
by European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Preliminary data from a phase I clinical trial of a new drug called NVL-520 for patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and other solid tumors, suggest that it may have the potential to both halt tumor growth by inhibiting a cancer-causing...
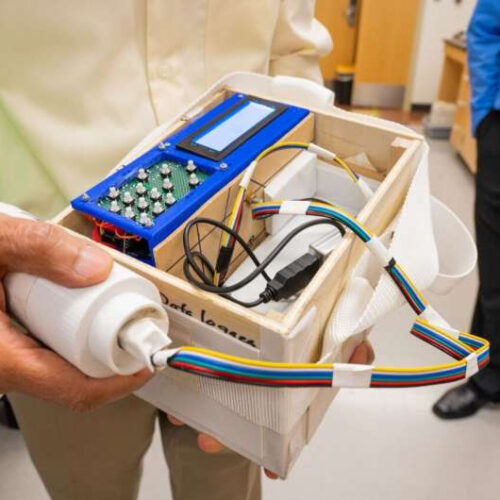
New tech aims to reduce racial disparities in blood measurements
by University of Texas at Arlington UTA and Shani Technologies are working on the device. Credit: University of Texas at Arlington A team led by a University of Texas at Arlington bioengineering professor and an Austin businessman has published key findings in the BMJ Innovations that illustrate how a new device measures hemoglobin more accurately in individuals...
How to tell whether you have athlete’s foot or eczema
Eczema and athlete’s foot cause similar symptoms, making them difficult to tell apart. However, eczema typically appears around the elbows and knees, while athlete’s foot typically affects the toes and feet. Despite their similar symptoms, the two conditions are unrelated. Environmental and genetic factors contribute to eczema, while athlete’s foot is the result of a...
Scientists find the brain cells that drive us to eat fat, sugar
Specific neurons in the brain may drive our overeating behavior. mikroman6/Getty Images Researchers investigated the neural activity underlying the consumption of fatty and sugary foods and activity levels. They looked at the effect of a specific cluster of neurons in the brain’s emotional center—the amygdala— on energy consumption and energy expenditure. They tested this by turning...
Healthy blood flow is more important than you may know
by University of California – San Diego Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain When UC San Diego bioengineering professor emeritus Shu Chien reminds you that it’s a good idea to get up, move, and get your blood flowing, he knows exactly what he is talking about. In fact, Chien has led research teams that discovered some of...
Fermented foods and fiber may lower stress levels, says new study
by John Cryan, The Conversation Foods such as kimchi are great to include in a psychobiotic diet. Credit: Nungning20/ Shutterstock When it comes to dealing with stress, we’re often told the best things we can do are exercise, make time for our favorite activities or try meditation or mindfulness. But the kinds of foods we...
Can you get addicted to melatonin?
by Barbara Brody, Rutgers University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Can you be addicted to chocolate? What about Pilates or checking your email? Although many of us use the word “addiction” fairly casually, from a medical perspective it requires meeting very specific criteria, and melatonin doesn’t have the chemical makeup to induce addiction in most people....
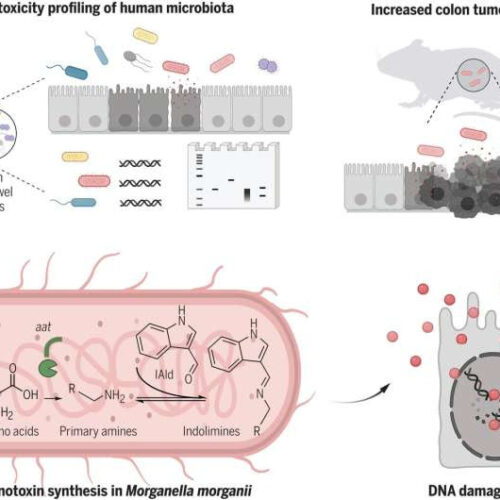
Family of DNA damage–inducing microbial metabolites found in guts of people with IBS
by Bob Yirka, Medical Xpress Human gut microbes isolated from IBD patients produce small-molecule genotoxins. Diverse gut microbes isolated from patients with IBD exhibit direct genotoxicity. M. morganii produces a family of genotoxic small molecule metabolites, termed the indolimines. Indolimine-producing M. morganii induces DNA damage in intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) and increased colon tumor burdens...
New drug elicits an antidepressant effect in mice in just two hours
by Bob Yirka, Medical Xpress Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain A team of researchers working at Nanjing Medical University in China, has developed a new antidepressant drug that elicits an antidepressant effect in mice in just two hours. In their paper published in the journal Science, the group describes their novel approach to treating depression. Chronic depression is one...