By Rich Haridy January 22, 2023 The VR sensory space offers a number of sensory room experiences Evenness A first-of-its-kind study has found adults with neurodevelopmental disabilities may experience improvements to symptoms of anxiety and depression after using specially designed virtual reality sensory rooms. Sensory rooms have been utilized for decades to help manage distress,...
Watch Your Words (To Ease Pain)
The right words from a doctor or nurse can reduce a patient’s pain, promote healing and calmness, and even encourage a patient to take medications properly. The prototype wristwatch here, called CommSense, offers meaningful, real-time ways to improve how doctors and nurses talk with their patients. Illustration by Sanjay Suchak, University of Virginia Communications But clinicians’...
Dietary nitrate – found in beetroot juice – significantly increases muscle force during exercise
UNIVERSITY OF EXETER A new study has found that consuming dietary nitrate – the active molecule in beetroot juice – significantly increased muscle force while exercising. While it is known that dietary nitrate enhances exercise, both boosting endurance and enhancing high-intensity exercise, researchers still have much to learn about why this effect occurs, and how our bodies convert...
Insulin underuse in primary care requires clinicians to remove barriers to patient access
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF FAMILY PHYSICIANS The rising cost of insulin has created problems in diabetes management. Researchers conducted a survey study to determine the prevalence of cost-related insulin underuse in a primary care environment. They examined the frequency of cost-related underuse of insulin within a year of a patient being diagnosed with diabetes. Ninety respondents...
Primary care practices implemented more care management processes despite the impact of COVID-19
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF FAMILY PHYSICIANS Although primary care clinics were disrupted by the COVID-19 pandemic, a study by Minnesota researchers showed that care management processes for chronic disease care in the primary care setting generally increased from 2019 to 2021. The team used data from 269 primary care clinics in 2017, 2019 and 2021, as...
Tool for UTI detection performs well in primary care setting, may reduce unnecessary antibiotics use
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF FAMILY PHYSICIANS Urinary tract infections (UTI) are commonly diagnosed and treated in primary care. The gold standard for diagnosing a UTI is a urine culture. However, waiting for culture results delays treatment, so doctors often prescribe antibiotics while awaiting those results. Researchers modified a UTI detection algorithm developed and validated in an...
Comprehensive primary care, accessibility and continuity can reduce hospitalizations
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF FAMILY PHYSICIANS Japanese researchers examined the association between primary care practice characteristics and total hospitalizations during the COVID-19 pandemic. They conducted a nationwide study and examined data from 1,161 participants ages 40-75. They assessed the quality of primary care attributes, including first contact between the patient and a primary care clinician, length of care,...
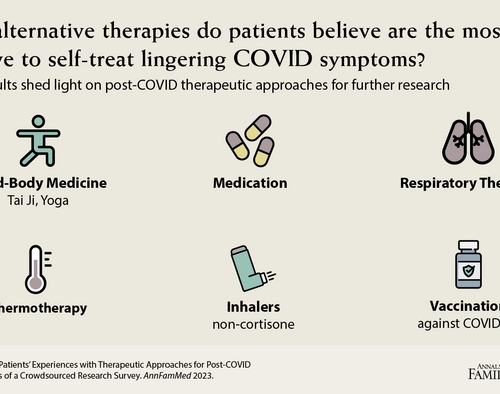
Primary care plays a role in helping patients with long COVID symptoms by providing holistic, trustworthy care
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF FAMILY PHYSICIANS IMAGE: KLOCKE, C. PATIENTS’ EXPERIENCES WITH THERAPEUTIC APPROACHES FOR POST-COVID SYNDROME: RESULTS OF A CROWDSOURCES RESEARCH SURVEY CREDIT: ANNALS OF FAMILY MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN Many people are experiencing a variety of long COVID-19 symptoms and are relying on some of their own methods to allay those symptoms. Others are...
Scientists explain emotional ‘blunting’ caused by common antidepressants
by University of Cambridge Credit: CC0 Public Domain Scientists have worked out why common anti-depressants cause around half of users to feel emotionally “blunted.” In a study published today in Neuropsychopharmacology, they show that the drugs affect reinforcement learning, an important behavioral process that allows people to learn from their environment. According to the NHS, more...
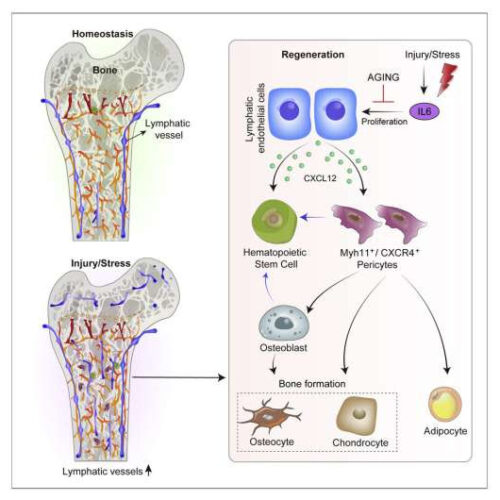
Role of lymphatic system in bone healing revealed
by University of Oxford Graphical Abstract. Credit: Cell (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.12.031 It was previously assumed that bones lacked lymphatic vessels, but new research from the MRC Human Immunology Unit at Oxford’s MRC Weatherall Institute for Molecular Medicine not only locates them within bone tissue, but demonstrates their role in bone and blood cell regeneration and reveals changes...