AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY Skiers, hikers, soldiers and others exposed to extreme cold temperatures can experience frostbite — a painful injury that occurs when ice crystals form in the skin. Many extremely cold areas are also remote, and delays in frostbite treatment can result in severe wounds, scarring and even limb amputation. Now, researchers reporting in...
Just in the NIK of time
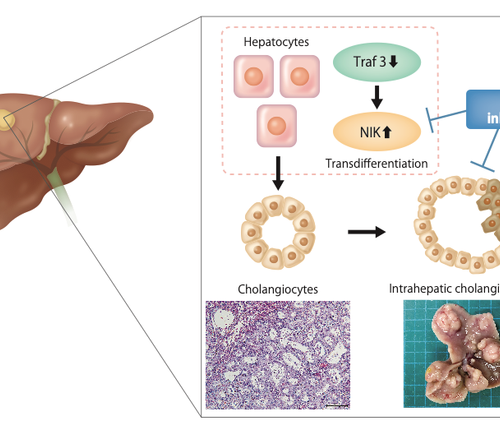
OSAKA UNIVERSITY IMAGE: NOVEL MECHANISM OF INTRAHEPATIC CHOLANGIOCARCINOMA DEVELOPMENT THROUGH TRANSDIFFERENTIATION OF HEPATOCYTES THROUGH DYSREGULATION OF TRAF3/NIK SIGNALING. CREDIT: YUTO SHIODE ET AL. Osaka, Japan – In a recent article published in Hepatology, a group led by researchers at Osaka University investigated the molecular mechanisms that drive development of Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) – a cancer which...
New device developed for easier link between brain, computer, and body
SKOLKOVO INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (SKOLTECH) Scientists from Skoltech, South Ural State University, and elsewhere have developed a device for recording brain activity that is more compact and affordable than the solutions currently on the market. With its high signal quality and customizable configuration, the device could help people with restricted mobility regain control...
Magnesium is essential for the immune system, including in the fight against cancer
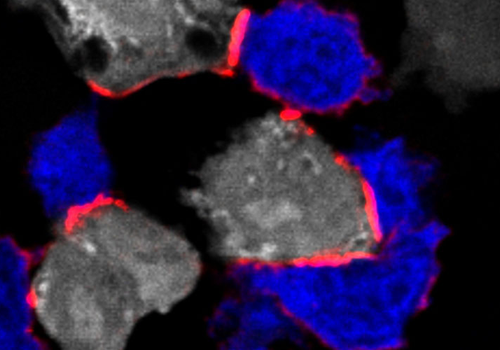
UNIVERSITY OF BASEL IMAGE: IMMUNOFLUORESCENT IMAGE DEPICTING T CELLS (BLUE) ATTACKING TUMOR CELLS (WHITE) BY FORMING AN IMMUNE SYNAPSE WITH LFA-1 (OPEN HEADPIECE CONFORMATION – LABELED IN RED). A NEW STUDY IDENTIFIED EXTRACELLULAR MAGNESIUM AS A CRITICAL IMMUNE MODULATOR OF CD8+ T CELLS. CREDIT: J. LOETSCHER ET AL., CELL (2022) The level of magnesium in...
The Xa Factor: pushing back on Atherosclerosis
TOKYO MEDICAL AND DENTAL UNIVERSITY VIDEO: THE XA FACTOR: PUSHING BACK ON ATHEROSCLEROSIS CREDIT: ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR YASUHIRO MAEJIMA, TMDU New research by a team led by researchers from the Department of Cardiovascular Medicine at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU); and the Department of Cardiovascular Medicine at Tokyo Kyosai Hospital has opened up interesting pathway...
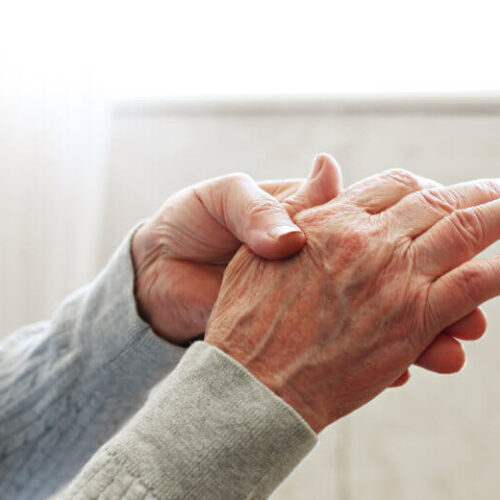
Scientists find potential cure for arthritis pain — by using electricity to regrow cartilage
HEALTH & MEDICAL, SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY JANUARY 17, 2022 by Study Finds STORRS, Conn. — A new method of regrowing cartilage by zapping the bone could bring pain relief to millions of people who suffer from arthritis. The technique, which researchers at the University of Connecticut have successfully tested on rabbits, uses small electric shocks to stimulate...
Mild COVID cases still lead to attention and memory issues
by Reuters Wednesday, 19 January 2022 00:01 GMT By Alistair Smout LONDON, Jan 19 (Reuters) – People with mild COVID-19 who do not suffer any other traditional “long COVID” symptoms can still exhibit deteriorated attention and memory six to nine months after infection, a study by Britain’s Oxford University has found. Cognitive issues impacting concentration...
Partial bone marrow transplant ‘rescues’ mice with cystic fibrosis
by La Jolla Institute for Immunology A partial bone marrow transplant helps these mice by introducing a population of healthy immune cells called monocytes. Credit: La Jolla Institute for Immunology Scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) have found they can dramatically improve survival of mice with cystic fibrosis through a partial bone marrow...
Researchers pinpoint how Zika virus evades cell’s antiviral response
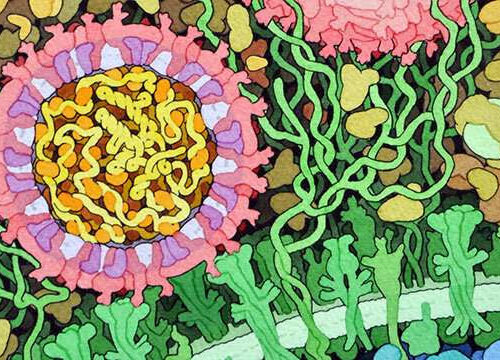
by Megan Fellman, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Cross-section of Zika virus. Credit: David Goodsell The world knows SARS-CoV-2 intimately now, but there are more than 200 virus species capable of infecting humans and causing disease. And they all want to do the same thing: Invade the host cells, hijack each cell’s machinery and...
Research boosts case for new gene therapy to treat severe form of epilepsy
by Josh Barney, University of Virginia Credit: CC0 Public Domain Research from the University of Virginia School of Medicine suggests how a newly developed gene therapy can treat Dravet syndrome, a severe form of epilepsy, and potentially prolong survival for people with the condition. The gene therapy, developed by Stoke Therapeutics, is now in clinical...