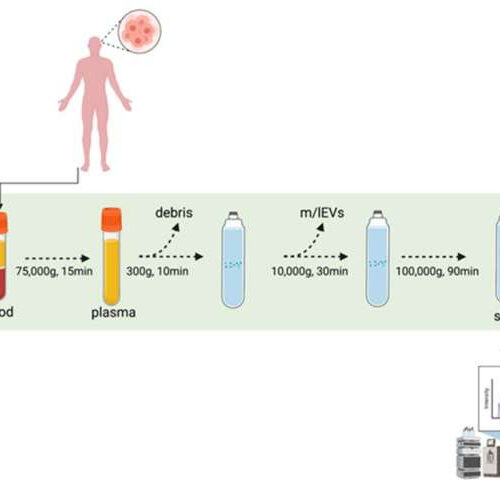
JANUARY 17, 2022 by University of Sussex Figure 1. Experimental pipeline. sEVs from GB patients and healthy volunteers’ blood samples were isolated through UC. The proteomic content of the sEVs were deciphered using mass spectrometry. Figure was created using BioRender.com. Credit: DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10010125 Researchers at the University of Sussex are one step further to developing a...
Arthritis-related gene also regenerates cartilage in joints and growth plates
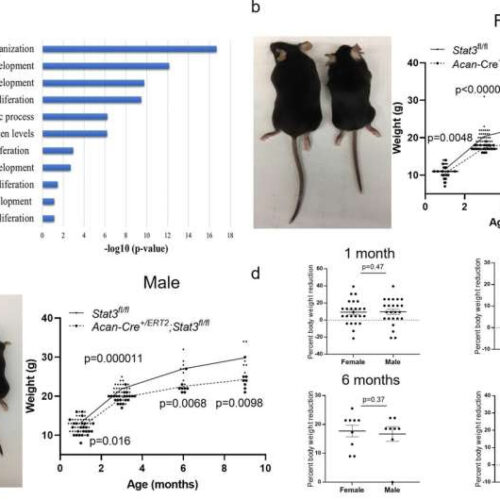
JANUARY 17, 2022 by Cristy Lytal, University of Southern California Fig. 1: STAT3 regulates anabolic genes in human fetal chondrocytes and body size in mice. a Altered gene expression in human fetal chondrocytes after knockdown of STAT3 by shRNA in vitro as determined by bulk RNA-Seq and GO analysis; n = 3. Postnatal deletion of Stat3 in chondrocytes...
Scientists found a way to break down defences of antibiotic resistant bacteria
Antibiotic resistance makes our medicine useless against common bacterial infections. This is a dangerous situation, which leads to increased doses of common antibiotics. Scientists are looking for new medicine and even ways for introducing genetic mutations to bacteria to reduce their resistance. But an international team of researchers have a different alternative solution – existing...
Obesity in mice lowered by increasing effects of key weight-regulating hormone
JANUARY 17, 2022 by University of Michigan Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Blocking the activity of an enzyme inside fat cells can decrease obesity and related health disorders in mice, according to new research led by the University of Michigan Life Sciences Institute. The study, published online Jan. 17 in the journal Nature Metabolism, focused on an enzyme...
Sugar detox? Cutting carbs? A doctor explains why you should keep fruit on the menu
by Jennifer Rooke, The Conversation Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain One of my patients—who had been struggling with obesity, uncontrolled diabetes, and the cost of her medications—agreed in June 2019 to adopt a more whole-food plant-based diet. Excited by the challenge, she did a remarkable job. She increased her fresh fruit and vegetable intake, stopped eating...
The circadian clock in heart failure
by Baylor College of Medicine Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Disrupting circadian rhythms, which change naturally on a 24-hour cycle, has been implicated in heart disease, but it is unclear how it leads to the condition. A research team at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions investigated the function of the protein Rev-erbα/β, a key...
Dementia cases set to triple by 2050
New research predicts the global burden of dementia by 2050. Catherine MacBride/Stocksy Globally, about 153 million people will have dementia by 2050, according to a new study. Risk factors such as smoking, obesity, and high blood sugar could be responsible for almost 7 million of these cases. Estimated increases of dementia cases in the Middle...
Long COVID: Could antiplatelet therapy help?
New research suggests that antiplatelet therapy and anticoagulants may help treat people with long COVID. Tara Moore/Getty Images Scientists know little about the underlying mechanisms of long COVID despite widespread reports about it since near the start of the pandemic, This lack of knowledge has made diagnosing and developing treatments for this condition challenging. COVID-19...
Personalized medicine – Functioning, induced liver cells from skin tissue
INSELSPITAL, BERN UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL The urea cycle is responsible for removing nitrogenous waste produced from the breakdown of protein in the organism. If the OTC enzyme is missing in this cycle, ammonia accumulation rises to toxic levels. An OTC deficiency is the most common disorder in the urea cycle. It could not be cured with...
Unprecedented cellular maps of tissues enabled by new tool
Ability to combine cell function and spatial information key to understanding life at molecular level and making cellular maps of tissues. The study of the human body at single-cell level has received a boost with the creation of a new tool, which will allow researchers to see not only the function of cells, but also...