UNIVERSITÉ LAVAL Québec City, January 10, 2022 – A team of Université Laval scientists may have discovered why severe depression affects women and men differently, according to a study published today in Nature Communications. The researchers examined the brains of people with depression at the time of death and discovered alterations located in different parts of the...
Less than 1 in 5 adults with Type 2 diabetes in the U.S. are meeting optimal heart health targets
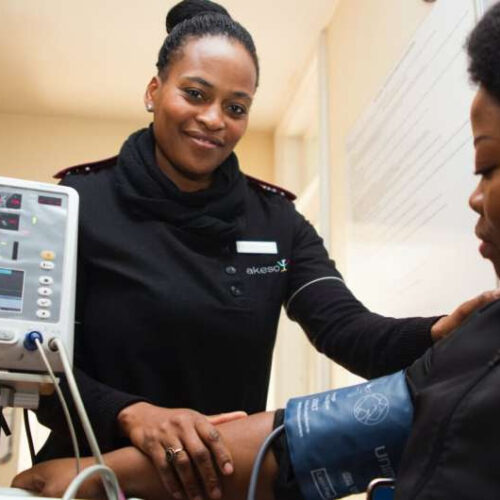
AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION DALLAS, Jan. 10, 2022 — Fewer than 1 in 5 adults with Type 2 diabetes in the U.S. are meeting targets to reduce heart disease risk. Fortunately, available therapies can help when combined with new approaches that address social determinants of health and other barriers to care, according to a new American...
Study sets framework for precision surveillance of colorectal cancer
by Tom Wilemon, Vanderbilt University Medical Center Credit: CC0 Public Domain A team of Vanderbilt researchers has revealed some of the mechanisms by which polyps develop into colorectal cancer, setting the framework for improved surveillance for the cancer utilizing precision medicine. Their study, published Dec. 14 in Cell, describes findings from a single-cell transcriptomic and imaging...
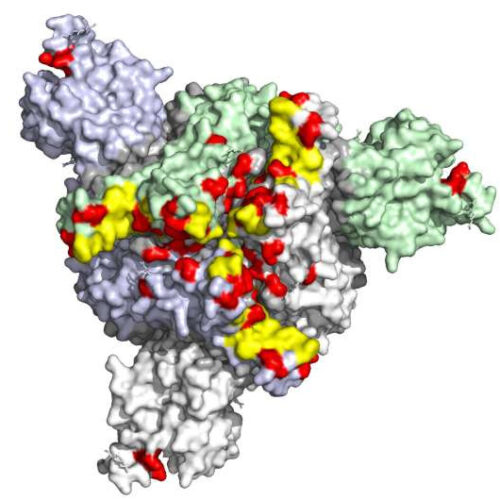
Omicron resistant to most monoclonal antibodies but neutralized by a booster dose
by Pasteur Institute 3D visualization of mutations in the spike protein of the Omicron variant. Left: overhead view. Right: lateral view. Mutations are indicated in red. They occur all over the spike protein but particularly in the receptor binding domain (RBD) and in the region known as the N-terminal domain (NTD). Credit: Institut Pasteur –...
Improving care for people with rare neuroendocrine tumors
by Flinders University Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain A revolutionary new way of caring for people with neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) will be trialed in the coming months, with the Flinders University-led project aiming to improve patient quality of life and develop a cost-effective system that can be implemented across other rare cancers in the future. The...
Feeling powerless in the pandemic? Four self-determination principles can help you take back some control
by Kate Mulligan, The Conversation Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain The omicron wave seemed to come like a rising tide—slowly, then suddenly, in all directions and all at once. Inside the health-care system, skeleton crews face impossible workloads and moral distress. Outside of it, people are feeling the weight of things like deferred care, deprioritized essential workers, online learning and doomscrolling. People are sick not...
Study shows climate change will lead to increase in kidney stones
by Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Rising temperatures due to climate change will lead to an increase in cases of kidney stones over the next seven decades, even if measures are put in place to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, according to a new study by researchers at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP)....
Study reveals how triclosan, likely found in toothpaste, is triggered to harm the gut
by University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain A new study conducted in mice demonstrates precisely how triclosan, an antimicrobial found in toothpaste, toys and thousands of other products, can trigger gut inflammation. An international team of researchers led by the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, the University of Massachusetts Amherst...
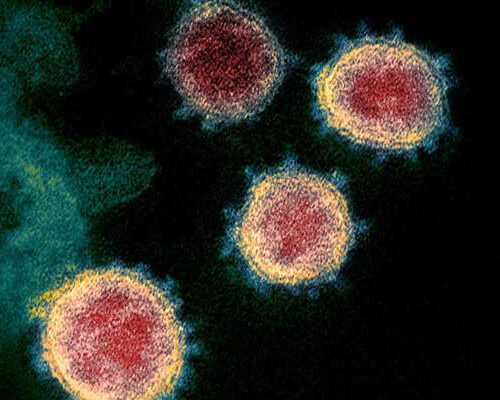
T cells from common colds cross-protect against infection with SARS-CoV-2
by Imperial College London A colorized scanning electron micrograph of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Credit: NIAID A new study, published in Nature Communications and led by Imperial College London researchers, provides the first evidence of a protective role for these T cells. While previous studies have shown that T cells induced by other coronaviruses can recognize SARS-CoV-2, the...
Scientists discover a new type of heart cell
Scientists have identified a new type of heart cell. Elva Etienne/Getty Images Disturbances in a newly discovered type of heart cell may underlie certain congenital heart abnormalities and a broader array of autonomic nervous system conditions. The cells, called cardiac nexus glia, were shown to play an important role in both heart rate and heart...