After you finish a milkshake or a bowl of guacamole, those dietary fats have a typical route through your body. New research from the laboratory of Dr. Natasza Kurpios, associate professor in the Department of Molecular Medicine in the Cornell College of Veterinary Medicine, has now revealed a key molecular mechanism that can send those fats on the...
Psilocybin, in 10mg or 25mg doses, has no short- or long-term detrimental effects in healthy people
KING’S COLLEGE LONDON New research from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology, & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King’s College London, in partnership with COMPASS Pathways, has established that psilocybin can be safely administered at doses of either 10mg or 25mg to up to six participants simultaneously. The research, published in The Journal of Psychopharmacology, is an essential...
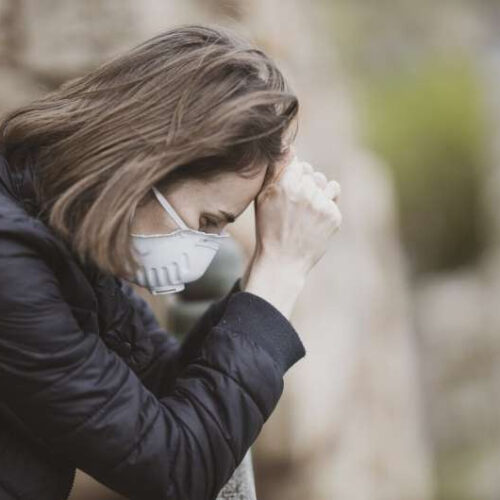
COVID-19 and PTSD: Assessing the pandemic’s toll on mental health
by Yale University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Illness, grief, job loss, social isolation, uncertainty, and other pandemic-driven stressors have contributed to an increase in psychological distress on an unusually wide scale. As researchers and clinicians continue to grapple with the psychological fallout from COVID-19, a growing body of literature has examined the prevalence of post-traumatic...
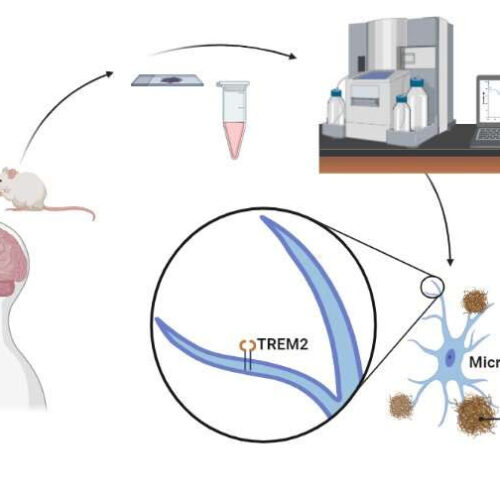
Research clears up how brain ‘cleaners’ fail in ALS
by Mayo Clinic Using samples donated to Mayo Clinic’s Brain Bank for Neurodegenerative Disorders, as well as mouse models, biochemistry, confocal microscopy, and computational simulations, researchers showed that a receptor on microglial cells, called TREM2, can clear a protein that builds up in the brains of patients with ALS. Image created with BioRender. Credit: Mayo...
Early data for multivariant COVID-19 vaccine booster shows promise
by Mike Addelman, University of Manchester Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain The first results of an early trial of a multivariant COVID-19 vaccine booster, launched in Manchester in September 2021, has shown it is driving a comprehensive immune response. U.S.-based biotechnology company Gritstone bio, Inc. in collaboration with The University of Manchester and Manchester University NHS Foundation...
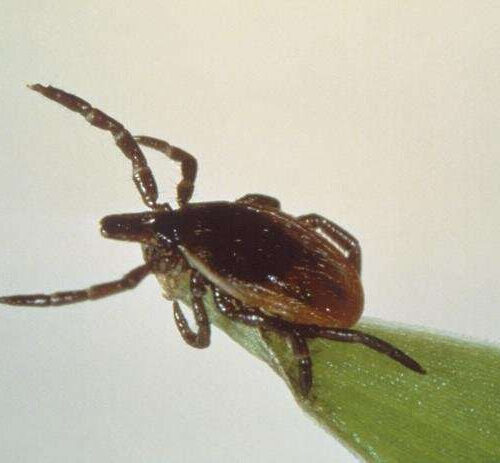
New tool emerging in fight against Lyme disease
by Carol Thompson Host-seeking blacklegged tick. Credit: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), CC0 As black-legged ticks crawl their way across Michigan, scientists hope a new vaccine in development could make their presence less menacing. The vaccine would rob the ticks of a trait that makes them exceptional vectors for Lyme disease: the ability to bite and...
Do you have ‘COVID-somnia’? These sleep tips might help
(HealthDay)—If the pandemic is causing you to lose sleep at night, you’re not alone. About 56% of Americans say they have what experts have dubbed “COVID-somnia,” an increase in sleep disturbances. Of people reporting these disturbances, 57% say they’re having trouble falling or staying asleep. About 46% are sleeping less; 45% are experiencing worse sleep; and 36%...
Cervical screening without a speculum boosts uptake among older patients
by King’s College London Credit: CC0 Public Domain Offering cervical screening without a speculum increases uptake among older women, new research has found. The study, published today in the British Journal of General Practice and led by Dr. Anita Lim from the School of Cancer & Pharmaceutical Sciences, was conducted at 10 GP practices in East London. A...
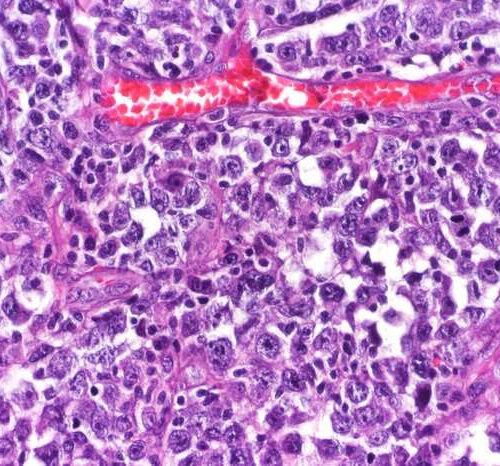
Lymphoma cell metabolism may provide new cancer target
by Weill Cornell Medical College Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Credit: CoRus13, distributed under a CC BY-SA 4.0 license Aggressive and relatively common lymphomas called diffuse large B cell lymphomas (DLBCLs) have a critical metabolic vulnerability that can be exploited to trick these cancers into starving themselves, according to a study from researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine...
Gene involved in sense of smell could play a role in the spread of breast cancer to the brain
by Massachusetts General Hospital Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain An olfactory receptor gene that aids in the sense of smell may also play a role in the metastasis of breast cancer to the brain, bones and lung, researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) have found. The team further discovered that inhibiting the gene, OR5B21, significantly decreased the...