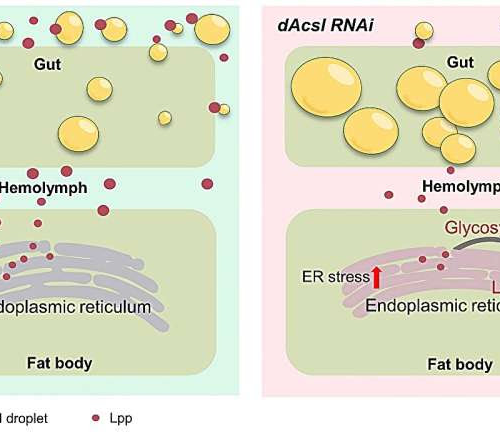
by Higher Education Press Working model for the role of dAcsl in the regulation of circulating lipoprotein level. Credit: Jie Li, Yue Dong, Tianxing Zhou, He Tian, Xiahe Huang, Yong Q Zhang, Yingchun Wang, Sin Man Lam, Guanghou ShuiInterorgan lipid transport is crucial for organism development and the maintenance of physiological function. Drosophila long-chain acyl-CoA...
Category: <span>Metabolic</span>
Team develops a single-nucleus resolution atlas of white adipose tissue in different depots
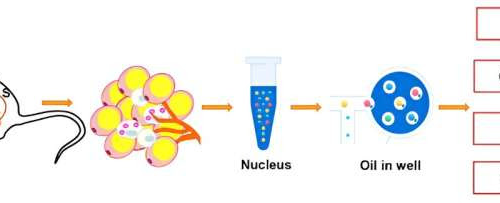
by Higher Education Press Workflow to perform snRNA-seq of different WAT depots. The nuclei were derived from subcutaneous (S), epididymal (E), mesenteric (M), peri-nephritic (N), and peri-heart (H) adipose depots, which were pooled from 40 male C57BL/6J mice. Sequencing data went through the quality control process (described in the section of Materials and methods of...
How obesity dismantles our mitochondria: Study reveals key mechanism behind obesity-related metabolic dysfunction
by University of California – San Diego These colored streaks are mitochondrial networks within fat cells. Researchers from UC San Diego discovered that a high-fat diet dismantles mitochondria, resulting in weight gain. Credit: UC San Diego Health SciencesThe number of people with obesity has nearly tripled since 1975, resulting in a worldwide epidemic. While lifestyle factors...
Breaking down fat byproducts could lead to healthier aging: Researchers identify key enzyme that does just that
by Eyleen Jorgelina O’Rourke, The Conversation Triacylglycerols, also known as triglycerides, are composed of a glycerol linked to three fatty acids. Credit: Lumen Learning (formerly Boundless) via LibreTexts, CC BY-SAThe journey of aging brings with it an unavoidable reality for many: an increased accumulation of body fat. Though much of society seems mostly focused on the...
Study provides insights into role of ‘hunger hormone’ receptor in obesity-related chronic inflammation
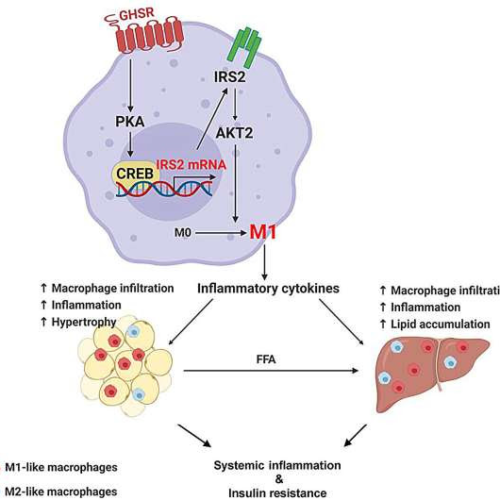
by Laura Muntean, Texas A&M University Credit: Molecular Metabolism (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2023.101852A team comprised primarily of Texas A&M AgriLife Research scientists has made an important discovery that could lead to a novel treatment for obesity and obesity-associated diseases or conditions. Details of the discovery can be found in the study “Nutrient-sensing growth hormone secretagogue receptor in...
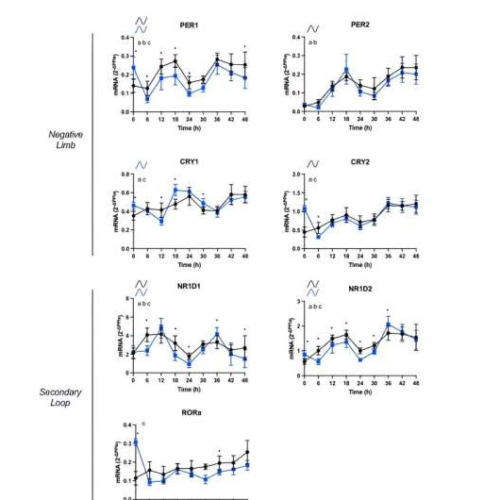
Effects of resveratrol on circadian clock gene expression in young and older human cells
by Impact Journals LLC Resveratrol increases in vitro rhythmic gene mRNA expression of core clock components in human adipose-derived progenitor cells (APCs) from older participants. Credit: Aging (2024). DOI: 10.18632/aging.205292A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging titled, “Effects of resveratrol on in vitro circadian clock gene expression in young and older...
Why Do GLP-1 Drugs Stop Working, and What to Do About It?
Marilynn Larkin There’s no question that glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists represent a major advance in the treatment of obesity for patients with or without diabetes. In clinical trials, participants lost 15%-20% of their body weight, depending on the drug. But studies also have shown that once people stop taking these drugs — either by...
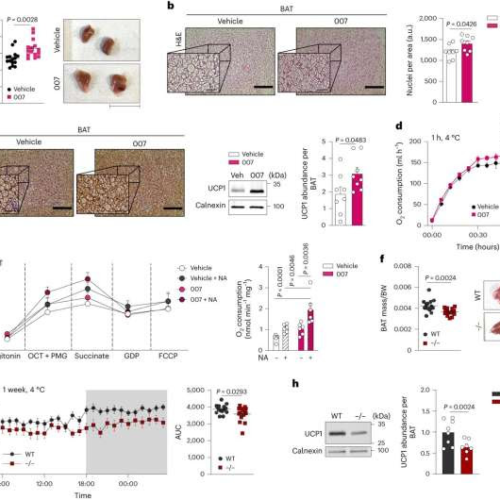
Researchers identify protein that increases the formation of good brown fat
by Inka Väth, University Hospital Bonn EPAC1 signaling promotes BAT growth and function in vivo. Credit: Nature Cell Biology (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41556-023-01311-9Brown fat cells convert energy into heat—a key to eliminating unwanted fat deposits. In addition, they also protect against cardiovascular diseases. Researchers from the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and the Transdisciplinary Research Area “Life &...
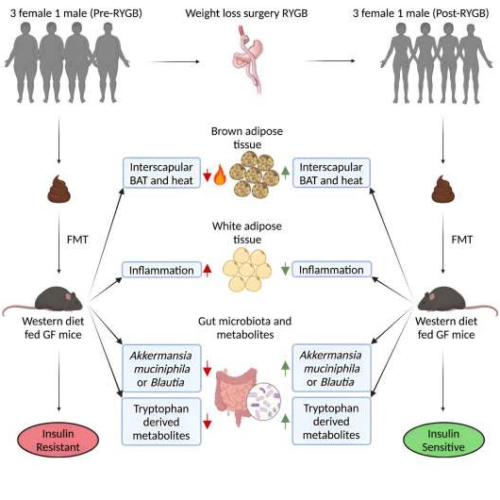
Researchers explore changes to microbiome following weight-loss surgery
by Jim Oldfield, University of Toronto Graphical abstract. Credit: Cell Reports Medicine (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101051Researchers at the University of Toronto and its partner hospitals are finding that changes in gut microbiota after bariatric surgery can directly improve metabolism, independent of food intake, weight loss and other metabolic factors. Their ongoing work—including a study published in the...
Study: Spinal cord injury causes acute and systemic muscle wasting
Peer-Reviewed Publication OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY WEXNER MEDICAL CENTER AN SCHWAB, MD, PHD, IS THE WILLIAM E. HUNT & CHARLOTTE M. CURTIS CHAIR AND A PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSCIENCES AT THE Ohio State College of Medicine. SCHWAB IS ALSO MEDICAL DIRECTOR OF THE Belford Center for Spinal Cord Injury AND A SCHOLAR OF THE CHRONIC...