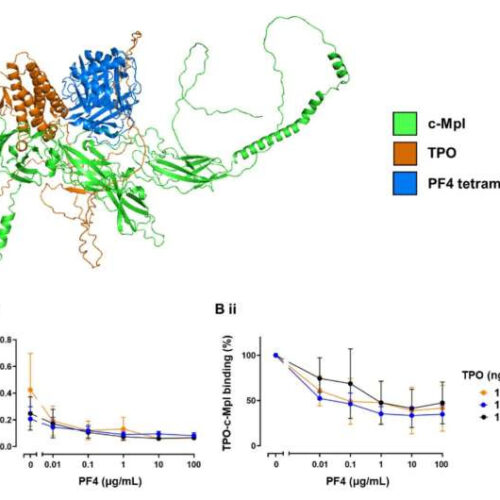
by University of Birmingham PF4 binding to c-Mpl disrupts TPO binding. (A) AlphaFold prediction of the binding of PF4 and TPO to c-Mpl. Overlayed cartoon structures of c-Mpl (green) complexed with either PF4 (blue) or TPO (orange) as modeled using Colabfold. Structure predictions were ranked by pLDDT, a per-residue measure of the confidence of the predicted...
Category: <span>Proteomics</span>
Key signaling protein identified as possible target for new therapies in hard-to-treat cancers
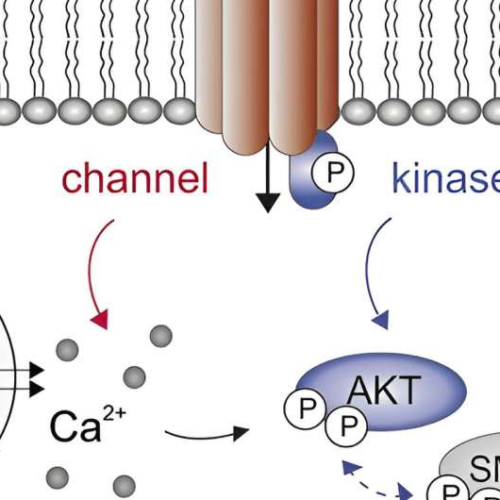
by American Physiological Society Credit: Function (2023). DOI: 10.1093/function/zqad053The unique signaling protein known as TRPM7 can stimulate and interact with an important cellular signaling hub called the AKT machinery, which is a well-known component of multiple cellular functions that drive growth and proliferation. This interaction causes a significant increase in the gene expression of COX-2, an...
Unexpected link found between 2 schizophrenia risk proteins
by Emily Caldwell, The Ohio State University Behavioral alterations in MAP6−/− and Kv3.1−/− mice. Adult (3–6 months old) WT B6 (black bars), MAP6−/− (red bars), and Kv3.1−/− (green bars) mice were used in a series of behavioral assays. Each group contained approximately half male and half female mice. a Example traces in the elevated plus maze...
Scientists identify cancer kill ‘switch’ that destroys tumours from the inside out
US researchers spotted a ‘switch’ that causes cancer cells to self-destructThe team now hopes to develop a treatment that targets this part of the cellBy EMILY CRAIG DEPUTY HEALTH EDITOR FOR MAILONLINE PUBLISHED: 05:45 EDT, 25 October 2023 | UPDATED: 05:45 EDT, 25 October 2023 A kill ‘switch’ which triggers the death of cancer cells...
Scientists discover a previously unknown way cells break down proteins
HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL At a glance: Scientists have discovered a previously unknown mechanism by which cells break down proteins that are no longer needed.These proteins are short-lived and modulate genes that support important neural, immune, and developmental processes.The mechanism could inform the design of therapies to treat conditions that arise when cells make too much...
Artificial Intelligence tools shed light on millions of proteins
UNIVERSITY OF BASEL IMAGE: A SNAPSHOT OF THE INTERACTIVE NETWORK “PROTEIN UNIVERSE ATLAS”. CREDIT: UNIVERSITY OF BASEL, BIOZENTRUM A research team at the University of Basel and the SIB Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics uncovered a treasure trove of uncharacterised proteins. Embracing the recent deep learning revolution, they discovered hundreds of new protein families and even...
Promising new approach targets aggressive type of prostate cancer
By Paul McClure August 14, 2023 Researchers have uncovered the pathway that leads to an aggressive form of prostate cancer and a potential treatment for it Depositphotos Researchers have uncovered the molecular mechanism that drives an aggressive form of prostate cancer that doesn’t respond well to typical treatments. Importantly, they also identified a drug currently undergoing...
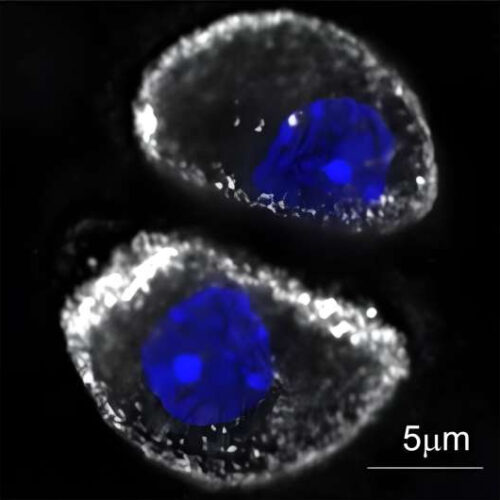
Research identifies protein that protects healthy joints from osteoarthritis
by University of Delaware The blue area is the cell nucleus, the white area is F-actin, the structural scaffolding of the cells. Researchers discovered adseverin regulates the amount of F-actin in the cells. In osteoarthritis loss of F-actin can eventually lead to cell death. Credit: University of Delaware A previously unstudied protein in the framework of...
Researchers identify protein that may help protect against osteoporosis
WILEY New research published in The FASEB Journal indicates that increasing the expression of a particular gene may help to prevent bone loss associated with postmenopausal osteoporosis. For the study, investigators examined which genes are involved in turning precursor cells called bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) into cells that play a crucial role in bone formation. The screen...
Unraveling a Protein That May Inspire a New Biotechnology Tool
Scientists have unraveled the step-by-step activation process of a protein with a deep evolutionary history in all domains of life, opening the door to harnessing its functions for use as a biotechnology tool. The protein belongs to the “superfamily” of Argonaute proteins, which previous research has suggested to be involved in gene silencing, a fundamental process known as RNA interference....